Configuring a Windows 95 Dial-Up Server
With Dial-Up Networking, you can configure a computer running Windows 95 to be a remote access server for dial-up clients running Windows 95, Windows for Workgroups, or Windows 3.1. The Windows 95 dial-up server can act as a gateway to an IPX/SPX or NetBEUI network, or as a server to the client, sharing its file and printing resources with one dial-up client at a time.
Note
Dial-up server capabilities are only available if you purchase the Microsoft Plus! for Windows 95. For information, please contact your Microsoft sales representative.
A Windows 95 dial-up server differs from the Windows NT 3.5 dial up server in the following ways:
- Windows NT 3.5 Server can act as an IP router, and Windows 95 cannot. IP router capabilities permit accessing a TCP/IP network, such as the global Internet. Windows 95 provides all the protocols you need to connect to the Internet, but cannot act as an IP router. Consequently, you need to connect a computer running Windows 95 to a server with IP router capabilities in order to connect to the Internet.
- Windows NT 3.5 supports 256 remote connections, whereas Windows 95 provides one remote connection.
- Windows NT 3.5 allows you to remotely administer the remote access server, whereas Windows 95 requires you to use system policies to remotely administer the server. For more information about system policies, see Chapter 15, "User Profiles and System Policies."
The Windows 95 dial-up server supports the following remote access clients:
- Windows 95 dial-up client
- Windows for Workgroups
- Windows 3.1 RAS client
- Clients running PPP
A Windows 95 dial-up server with the appropriate network protocols installed can act as a NetBIOS gateway, as illustrated in the following graphic.
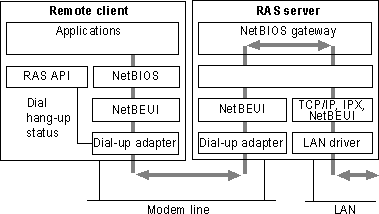
For more information about connectivity options of a Windows 95 dial-up server, see "Overview of Dial-Up Networking" earlier in this chapter.
Configuring a computer running Windows 95 to be a dial-up server consists of the following steps:
- Enabling File and Printer Sharing services for either Microsoft or NetWare networks on the dial-up server. For information, see Chapter 11, "Logon, Browsing, and Resource Sharing."
- Enabling user-level or share-level security on the dial-up server. For information, see "Using Security with Dial-Up Networking" later in this chapter.
- Configuring dial-up server capabilities in Dial-Up Networking. For information, see the following procedure.
To configure a computer as a dial-up server
- From the Connections menu in the Dial-Up Networking, click the Connections menu, and then click Dial-Up Server.
- In the Dial-Up Server dialog box, click Allow Caller Access. This dialog box will look different depending on whether you have enabled user-level or share-level security for the computer.
- Optionally, click Change Password to define a call-in password for Dial-Up Networking clients, and then click OK.
– Or –
If you are using user-level security for peer resource sharing, select the users who have access to this dial-up server. Then click OK.
- Click the Server Type button and then select the server type.
If you select the Default server type, the dial-up server will automatically start in PPP mode for incoming calls and switch to RAS for Windows NT 3.1 and Windows for Workgroups mode if the PPP negotiation fails. For information on PPP negotiation, see "PPP Dial-Up Sequence" later in this chapter.
- Click OK, and the dial-up server will be ready to answer incoming calls.
Notice that changes to the server type do not apply to a connection that is currently open. Changes will apply to any future connections made to this computer.
To disconnect any users who are currently connected to this computer through Dial-Up Networking
- In the Dial-Up Server dialog box, click the Disconnect User button.
Note The Windows 95 Dial-Up Server can use only one modem at a time. You can enable caller access on multiple modems at any one time, but only one modem can be connected.

