Setting the Domain Name System Server and IP Addresses
The Internet uses the Domain Name System (DNS) to translate computer and domain names into IP addresses. A DNS server maintains a database that maps domain names to IP addresses as specified by network administrators. The DNS organizes the names of hosts in a hierarchical fashion, similar to a file system. For more information, see Chapter 12, "Network Technical Discussion."
Before you can use TCP/IP to connect to the Internet, you need to configure a computer to recognize DNS information. Some Internet access providers dynamically assign IP addresses for DNS servers, but most do not. Most PPP Internet access providers do dynamically assign IP addresses. If an access provider does not dynamically assign either a DNS IP address or your IP address, you should set these in the TCP/IP Settings dialog box in Dial-Up Networking for each connection you create.
If, however, you have a static, direct LAN connection to the Internet or other TCP/IP network, then you should set the DNS IP address and your IP address in TCP/IP properties in the Network option in Control Panel. You do not need to set this information if your LAN's Internet access server dynamically assigns these to you; for example, if you are using a server with Dynamic Host Configure Protocol (DHCP) capabilities, such as a Windows NT 3.5 server, it will dynamically assign IP address information.
Note
The following procedures assume that your computer has Microsoft TCP/IP installed as a network protocol. If your site uses another vendor's version of TCP/IP, you must configure the protocol as recommended by the protocol vendor.
To set the DNS IP address if you have a direct LAN connection to the Internet
- In the Network option in Control Panel, click the Configuration tab.
- In the network component list, double-click TCP/IP for the network adapter.
- In the TCP/IP Properties dialog box, click the DNS Configuration tab.
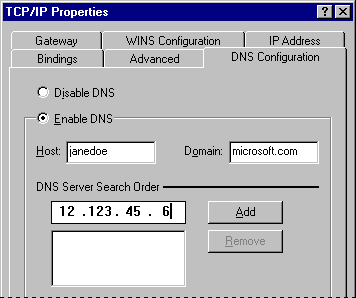
- Click Enable DNS, and then, in the Host and Domain boxes, type your host name and domain name, respectively. These names identify you on the Internet.
- In the DNS Server Search Order box, type the address of your LAN's DNS server in the DNS Server Search Order box.
If your network has more than one DNS server, type each DNS server and then click Add. DNS settings are currently global across all instances of TCP/IP. This allows you to rely on a secondary DNS server if the primary DNS server is down. The first server listed is the first one searched.
To set the DNS IP address for each connection in Dial-Up Networking
- In Dial-Up Networking, right-click the connection you defined for the Internet, and then click Properties.
- In the connection's properties, click Server Type, and then click TCP/IP Settings.

- In the TCP/IP Settings dialog box, click the option named Specify An IP Address, and type your IP address.
- Click the option named Specify Name Server Address, and then type the IP address of the DNS server in the Primary DNS box.
Important Because IP addresses identify nodes on an interconnected network, each host on the internetwork must be assigned a unique IP address, valid for its particular network.
To define your IP address if you have a direct LAN connection to the Internet
- In the Network option in Control Panel, double-click TCP/IP for the network adapter.
- In the TCP/IP Properties dialog box, click the IP Address tab, and then click the Specify An IP Address option.
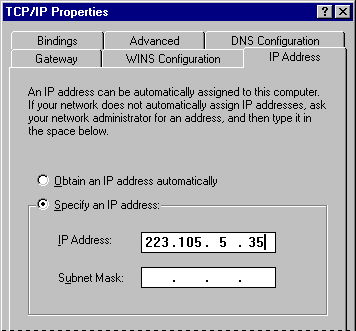
- In the IP Address box, type your IP address. After you type the address, your subnet mask will be provided automatically. Click OK.
To define your IP address if your access provider does not dynamically assign one
- In the TCP/IP Settings dialog box, click the option named Specify An IP Address, and then type your IP address.


