With Windows NT Server, the user accounts and global groups from one domain can be used in another domain. When a domain is configured to allow accounts from another domain to have access to its resources, it effectively trusts the other domain. The trusted domain has made its accounts available to be used in the trusting domain. These trusted accounts are available on Windows NT Server computers and Windows NT Workstation computers participating in the trusting domain.
Hint By using trust relationships in your multidomain network, you reduce the need for duplicate user account information and reduce the risk of problems caused by unsynchronized account information.
The trust relationship is the link between two domains that enables a user with an account in one domain to have access to resources on another domain. The trusting domain is allowing the trusted domain to return to the trusting domain a list of global groups and other information about users who are authenticated in the trusted domain. There is an implicit trust relationship between a Windows NT Workstation participating in a domain and its PDC.
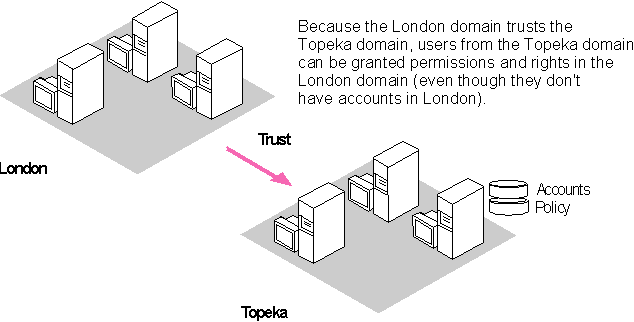
The following figure illustrates a trust relationship between two domains, where the London domain trusts the Topeka domain.

Figure 4.4 Trusted Domain
In this example, the following statements are true because the London domain trusts the Topeka domain:
When trust relationships are defined, user accounts and global groups can be given rights and permissions in domains other than the domain where these accounts are located. Administration is then much easier, because you need to create each user account only once on your entire network, and then the user account can be given access to any computer on your network (provided you set up domains and trust relationships to allow it).
Note Trust relationships can be configured only between two Windows NT Server domains. Workgroups and LAN Manager 2.x domains cannot be configured to use trust relationships.