RAS provides transparent network access for computer running Windows NT, Windows for Workgroups, MS-DOS version 3.1 or later (RAS version 1.1a), and MS OS/2 version 3.1 (RAS version 1.1).
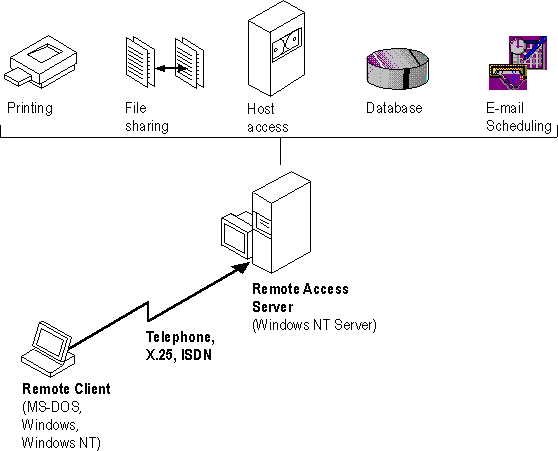
Users run the RAS graphical phone book on a remote computer, and then initiate a connection to the RAS server using a local modem, X.25, or ISDN card. The RAS server, running on a Windows NT Server-based computer connected to the corporate network, authenticates the users and services the sessions until terminated by the user or network administrator. All services that are typically available to a LAN-connected user (including file- and print-sharing, database access and messaging) are enabled via the RAS connection. The following figure depicts the RAS architecture:

Figure 9.1 RAS Architecture
Note that the remote clients use standard tools to access resources. For example, the Windows File Manager is used to make drive connections, and Print Manager is used to connect printers. Connections made while LAN-connected via these tools are persistent, so users don't need to re-connect to network resources during their remote sessions. Since drive letters and UNC (Universal Naming Convention) names are fully supported via RAS, most commercial and custom applications work without any modification.
Connectivity is achieved in one of three ways: via a standard modem, ISDN card, or X.25. The asynchronous modem is the most popular means of connecting, with ISDN emerging as a high-speed alternative. X.25 is a standard for many companies doing business internationally.