The name space for MIB objects is hierarchical. This structure allows assignment of a globally unique name to each manageable object.
Authority for parts of the name space is assigned to individual organizations. This allows organizations to assign names without consulting an Internet authority for each assignment. For example, the name space assigned to Microsoft is 1.3.6.1.4.1.311. Microsoft has the authority to assign names to objects anywhere below that name space.
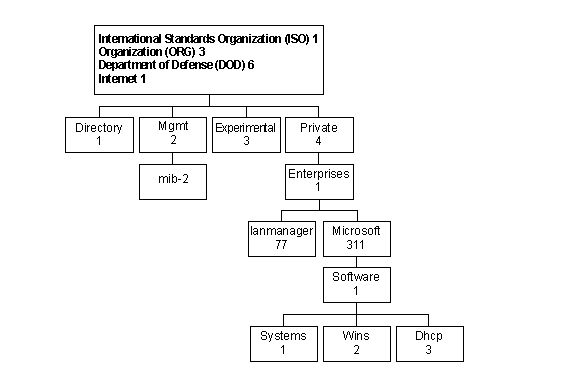
The following figure shows the name tree for the MIBs included with Windows NT.

The object identifier in the hierarchy is written as a sequence of labels beginning at the root and ending at the object. Labels are separated with a period. The following table shows the object identifier for each of the MIBs used in Windows NT.
MIB | Object name | Object number | Contents |
MIB_II.MIB | iso.org.dod.internet. | 1.3.6.1.2.1 | Defines objects essential for either configuration or fault analysis. Internet MIB II is defined in RFC 1213. |
LMMIB2.MIB | iso.org.dod.internet. | 1.3.6.1.4.1.77 | Defines objects that include such items as statistical, share, session, user, and logon information. |
— | iso.org.dod.internet. | 1.3.6.1.4.1.311.1.1 | Currently, there are no objects or DLL for this object name. |
WINS.MIB | iso.org.dod.internet. | 1.3.6.1.4.1.311.1.2 | Contains information for the WINS server, including statistics, database information, and push and pull data. |
DHCP.MIB | iso.org.dod.internet. | 1.3.6.1.4.1.311.1.3 | Contains statistics for the DHCP server and DHCP scope information. |
Note
The Windows NT SDK CD contains the source code for each of the Windows NT MIBs. See "SNMP Files on the SDK" in the "Programming Considerations" section later in this chapter for the filenames of the MIB files.