Statics Methods Relevant to GeometryBvr Objects
importGeometry(url) Creates a geometry behavior by synchronously importing the given .x file. importGeometry(url, geoStandIn, ev, progress, size) Creates a geometry behavior by asynchronously importing the given .x file. soundSource Creates a geometry behavior that contains the given sound behavior. spotLight Creates a spotlight geometry. union Creates a geometry behavior by combining the given geometries. unionArray Creates a geometry behavior by combining the geometries in the array.
importGeometry(url)
Statics Class
Creates a geometry behavior by synchronously importing the given .x file. Synchronous loads are blocking calls, which means that ticking will not continue on any model until all synchronous downloads are completed. These downloads should be small and listed before asynchronous downloads. Use asynchronous downloads for more complex images and sounds. See below for a description of the asynchronous import method.
Syntax
public static GeometryBvr importGeometry( URL url );
Parameters
- url
- Fully qualified path of the file to be downloaded. This parameter is of type java.net.URL.
Return Value
Returns the GeometryBvr object.
importGeometry(url, geoStandIn, ev, progress, size)
Statics Class
Creates a geometry behavior by asynchronously importing the given .x file. Asynchronous downloads should be listed after synchronous ones and used for more complex sounds and images. For a description of the synchronous import method, see above.
Syntax
public static GeometryBvr importGeometry(
URL url,
GeometryBvr geoStandIn,
DXMEvent[] ev,
NumberBvr[] progress,
NumberBvr[] size
);
Parameters
- url
- Fully qualified path of the geometry to be downloaded. This parameter is of type java.net.URL.
- geoStandIn
- Geometry to use while the contents at url are still being downloaded. This argument cannot be null.
- ev
- Event to trigger once the download is complete. This argument can be null.
- progress
- NumberBvr that goes from 0 to 1, tracking the progress of the download. For files downloaded via http, progress is reported as the percentage of the file that has been downloaded. For other protocols, the value may simply start at 0 and change to 1 once the download is complete. This argument can be null.
- size
- Size of the geometry, in bytes. The value begins at -1 and will change to the true size if it is available. This argument can be null.
Return Value
Returns the GeometryBvr object.
soundSource
Statics Class
Creates a geometry behavior that contains the given sound behavior. The bounding box is the empty bounding box, where the maximum coordinate is less than the minimum coordinate.
Syntax
public static GeometryBvr soundSource( SoundBvr sound );
Parameters
- sound
- SoundBvr object.
Return Value
Returns the GeometryBvr object.
spotLight
Statics Class
Creates a spotlight geometry. A spotlight is a positioned, directed light source initially located at the origin and directed along the negative z-axis.
Syntax
public static GeometryBvr spotLight( NumberBvr fullcone, NumberBvr cutoff );
Parameters
- fullcone
- NumberBvr object specifying the angle in radians from the main spotlight axis for which surfaces will receive full illumination from the light.
- cutoff
- NumberBvr object specifying the angle in radians from the main spotlight axis past which surfaces will receive no illumination from the light. This parameter can also be of type double.
Return Value
Returns the GeometryBvr object.
Remarks
Examples of real-world spotlights include desk lamps, headlights, and flashlights. The bounding box is the empty bounding box, where the maximum extent is less than the minimum extent.
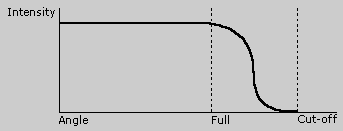
The fullcone parameter specifies the half-angle of the region that will receive the full intensity of the spotlight. This parameter can have values from 0.00 to pi.
The cutoff parameter specifies the half-angle of the region past which surfaces will receive no illumination. This parameter can have values from the value of fullcone to pi.
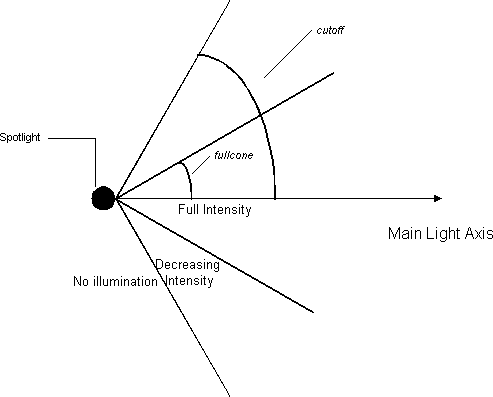
Surfaces receive illumination from the spotlight in the following manner:
- If the surface point is within fullcone radians of the main spotlight axis, the spotlight acts as a point light source (including distance attenuation effects).
- If the surface point is greater than fullcone radians, but is within cutoff radians of the main spotlight axis, the surface receives illumination that is attenuated by the angular displacement.
- If the surface point is greater than cutoff radians from the main spotlight axis, it receives no illumination.
These rules are illustrated in the following diagram.
The following diagram shows how the intensity of the spotlight changes in relationship to the angle:
union
Statics Class
Creates a geometry behavior by combining the given geometries. The new geometry contains all elements of the original geometries. The bounding box of a set of unioned geometries is simply the union of the bounding boxes of each of the geometries.
Syntax
public static GeometryBvr union( GeometryBvr g1, GeometryBvr g2 );
Parameters
- g1 and g2
- GeometryBvr objects.
Return Value
Returns the GeometryBvr object.
unionArray
Statics Class
Creates a geometry behavior by combining the geometries in the array. The new geometry contains all elements of the original geometries. The bounding box of a set of unioned geometries is simply the union of the bounding boxes of each of the geometries.
Syntax
public static GeometryBvr unionArray( GeometryBvr[], geometries );
Parameters
- geometries
- Array of GeometryBvr objects.
Return Value
Returns the GeometryBvr object.
 Top of Page
Top of Page
© 2000 Microsoft and/or its suppliers. All rights reserved. Terms of Use.