| Platform SDK: Transaction Server |
[This product will work only on Windows NT 4.0 versions and earlier. For Windows 2000 and later, see COM+ (Component Services).]
Retrieves the user name associated with the base process that initiated the sequence of calls from which the call into the current object originated.
Provided By
String getOriginalCallerName ( );
Return Values
User name associated with the the base process that initiated the call sequence from which the current method was called.
Remarks
You use the getOriginalCallerName method to determine the user name associated with the original process that initiated the call sequence from which the current method was called. The following scenario illustrates the functionality of the getOriginalCallerName method.

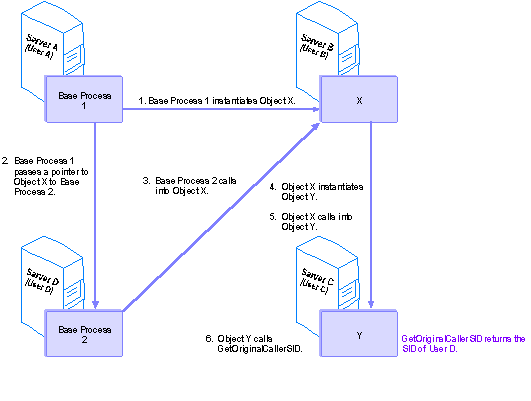
Base process 1, running on server A as user A, creates object X on server B, running as user B. Then base process 1 passes its reference on object X to base process 2, running on server D as user D. Base process 2 uses that reference to call into object X. object X then calls into object Y, running on server C. If object Y then calls getOriginalCallerName, the name of user D is returned.
Note Usually, an object's original caller is the same process as its original creator. The only situation in which the original caller and the original creator would be different is one in which the original creator passes a reference to another process, and the other process initiates the call sequence (as in the preceding example).
Note The path to the original caller is broken if any object along the chain was created by some other means than IObjectContext::CreateInstance or ITransactionContext::CreateInstance. For example, if base process 1 uses CoCreateInstance to create X, when Y calls getOriginalCallerName, the name it gets back will be the name of user B, not user D. This is because the call sequence is traced back through the objects' context and MTS can only create a context for an object that's created with either IObjectContext::CreateInstance or ITransactionContext::CreateInstance.
See Also
Programmatic Security, Advanced Security Methods, Context class