Multihomed computers — computers that run Windows NT Workstation and are connected to an intranet, and that also have one or more additional connections to the Internet — should comply with the security measures above, plus these additional precautions.
You should unbind unnecessary services from network cards connected to the Internet.
1. Double-click Network in Control Panel.
2. On the Bindings tab, show the bindings for all services, then select the binding under the service and click Disable.
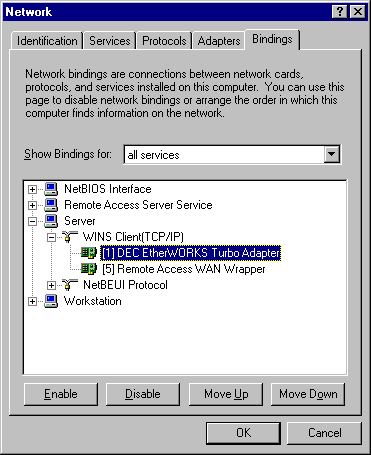
Figure 35.2 shows the Bindings tab of the Network dialog box.

Figure 35.2 The Bindings tab of the Network dialog box
For example, you might use the Server service to copy new images and documents from computers in your internal network on an Intel EtherExpress 16 LAN Adapter. However, when you are connected to the Internet using Dial-Up Networking, Internet users also have direct access to your computer through the Server service through the Remote Access WAN Wrapper binding as shown in Figure 35.2.
The Remote Access WAN Wrapper binding under the Server service should be disabled to prevent attacks through the Server service.
Note
You can use the Windows NT Server service over the Internet; however, you should fully understand the security implications and licensing issues. For more information about security and licensing, see Windows NT Server Concepts and Planning.
You should disable routing when you configure the TCP/IP protocol. If routing is enabled, you run the risk of passing data from your intranet to the Internet.
1. Double-click Network in Control Panel.
2. Click the Protocols tab, select TCP/IP Protocol, and click Properties.
3. On the Routing tab, clear the Enable IP Forwarding check box if it is selected.
Figure 35.3 shows the Routing tab with the Enable IP Forwarding check box cleared.
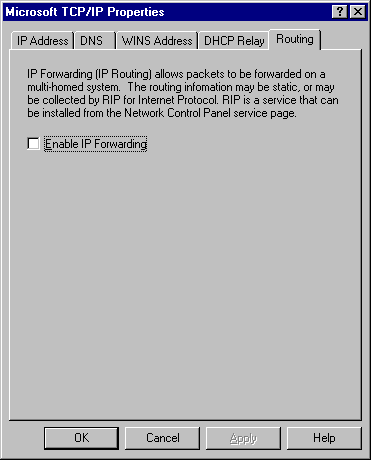
Figure 35.3 Disable routing by clearing the Enable IP Forwarding check box
On a default installation, you do not need to change any network shares. However, note that Windows NT Workstation automatically creates special shares for administrative and system use. For example, the root of every directory is shared to the Administrators, Backup Operators, and Server Operators groups. The share uses the convention
\\Computername\Driveletter$
For example, a share may be called \\maria2\c$. You cannot change this default setting. For more information about the default shares, see your Windows NT documentation.
If you do run the Server service on your Internet adapter cards, and you have created network shares, you should permit access only to those users and groups that you want to use the files. Double-check the permissions set on the shares you have created on the system. It is also wise to double-check the permissions set on the files contained in the shares' directories to ensure that you have set them correctly. In general, you should remove the group Everyone.
User Manager provides a way for the system administrator to specify how quickly account passwords expire (thus forcing users to regularly change passwords), and to set other policies, such as how many incorrect logon attempts are tolerated before a user is locked out. You should change the default settings. User Manager is used to set account policies. Pay particular attention to accounts with Administrator access. These steps help prevent exhaustive or random password attacks.