Security Information about Objects
All named (and some unnamed) objects in Windows NT can be secured. The security attributes for an object are described by a security descriptor. An object's security descriptor includes the following parts (as shown in Figure 6.5):
- An owner security ID, which indicates the user or group who owns the object. The owner of an object can change the access permissions for the object.
- A group security ID, which is used only by the POSIX subsystem and ignored by the rest of Windows NT.
- A discretionary access control list (ACL), which identifies which users and groups are granted or denied which access permissions. Discretionary ACLs are controlled by the owner of the object. (These are described later, in "Access Control Lists and Access Control Entries.")
- A system ACL, which controls which auditing messages the system will generate. (For more information about auditing objects, see "Auditing Security Events," later in this chapter.) System ACLs are controlled by the security administrators.
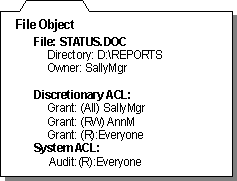
Figure 6.5 Security Descriptor for a File Object

