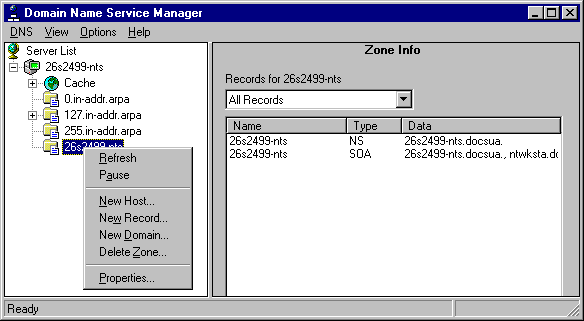
After you create a zone, you can add A, PTR, and other resource records for computers logically contained within the zone. To display a menu of actions that you can perform on the zone, point to the zone folder and right-click.
The two menu commands you can use to add information about the computers in the zone are New Host and New Record.

Figure 2.3 Zone Menu
You must use the New Host command to add A and PTR records for the zone computers that have statically assigned IP addresses. The A resource record provides the name-to-IP address mapping used in name resolution. The PTR resource record contains the reverse look-up (IP address - to - name) mapping that is needed by some programs.
The following figure illustrates the New Host dialog box.
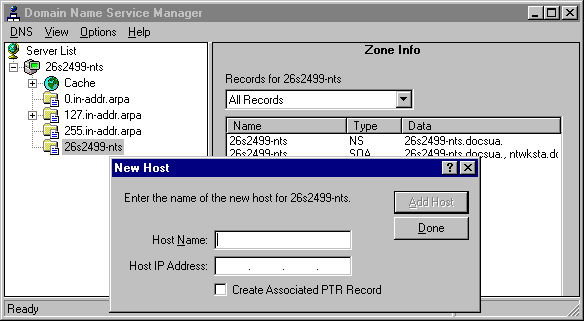
Figure 2.4 New Host dialog box
You use the New Record command to add other types of DNS resource records such as CNAME (alias), MX (mail exchange) or ISDN records.
The following figure illustrates the New Resource Record dialog box.
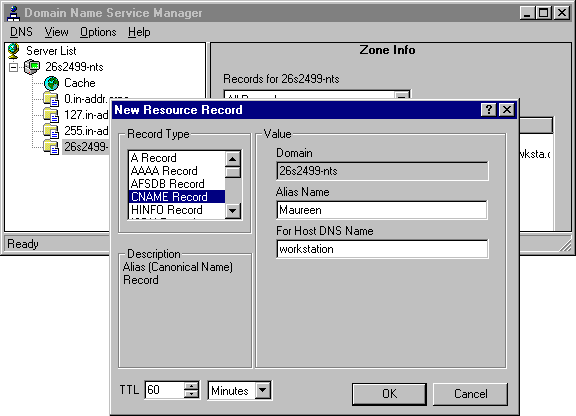
Figure 2.5 New Resource Record dialog box
The following table lists the types of resource records you can create and edit by using DNS Manager.
Table 2.2 DNS Resource Record Types
Record type | Description |
A | An address record that maps a host name to an IP address in a DNS zone. Its counterpart the PTR resource record is used to map an IP address to a host name in a DNS reverse lookup zone (those in the in-addr.arpa. DNS domain). It's important you add an A record for every computer in the zone that has a static IP address, including the local DNS name server and any computer running Internet Information Server. |
AFSDB | An address record that gives the location of either an Andrew File System (AFS) cell database server or a Distributed Computing Environment (DCE) cell's authenticated name server. The AFS system uses DNS to map a DNS domain name to the name of an AFS cell database server. The Open Software Foundation's DCE Naming service uses DNS for a similar function. |
Table 2.2 DNS Resource Record Types (Continued)
Record type | Description |
CNAME | A canonical name resource record, which creates an alias for the specified host name (that is, a name synonymous with the host name). You can use CNAME records to hide the implementation details of your network from the clients that connect to it. For example, in the Terra Flora case study used in the Windows NT Server Resource Kit, ftp.terraflora.com is an alias (that is, a CNAME) for the real name of the computer that runs the Terra Flora FTP server. A CNAME or alias also allows the FTP server to be moved easily to a different computer if necessary. If such a move is required, only the CNAME record need change, not the actual computer name. |
HINFO | The host information resource record, which identifies a host's hardware type and operating system. The CPU type and operating system identifiers used in an HINFO record should come from the list of computer and system names in RFC 1700. |
ISDN | The Integrated Services Digital Network (ISDN) resource record, a variation of the A resource record. Rather than mapping a host name to an IP address, the ISDN record maps the host name to an ISDN address. An ISDN address is a phone number that consists of a country code, an area code, a local phone number, and optionally a subaddress. Use the ISDN resource record in conjunction with the RT resource record, described following. |
MB | The mailbox resource record. This record, which is experimental, specifies a DNS host with the specified mailbox. Other related experimental records are the MG resource record, the MR resource record, and the MINFO resource record, all described following. |
MG | The mail group resource record. This record, which is experimental, specifies a mailbox that is a member of the mail group (that is, mailing list) specified by the DNS domain name. Other related experimental records are the MB resource record, the MR resource record, and the MINFO resource record. |
MINFO | The mailbox information resource record. This record, which is experimental, specifies the mailbox that is responsible for a specified mailing list or mailbox. Other related experimental records are the MB resource record, the MG resource record, and the MR resource record. |
MR | The mailbox rename resource record. This record, which is experimental record, specifies a mailbox that is the proper rename of the other specified mailbox. Other related experimental records are the MB resource record, the MG resource record, and the MINFO resource record. |
Table 2.2 DNS Resource Record Types (Continued)
Record type | Description | |
MX | The mail exchange resource record, which specifies a mail exchange server for a DNS domain name. A mail exchange server is a host that will either process or forward mail for the named DNS domain. Processing mail means either delivering it to the addressee or passing it to a different type of mail transport. Forwarding the mail means sending it to its final destination server, sending it by using Simple Message Transfer Protocol (SMTP) to another mail exchange server closer to its final destination, or queuing it for a specified amount of time. | |
NS | The name server resource record, which identifies the DNS server or servers for the DNS domain. NS resource records appear in all DNS zones and reverse zones (those in the in-addr.arpa DNS domain). | |
PTR | The pointer resource record, which maps an IP address to a host name in a DNS reverse zone (those in the in-addr.arpa DNS domain). Its counterpart, the A (address) resource record, is used to map a host name to an IP address in a DNS zone. | |
RP | The responsible person resource record, which indicates who is responsible for the specified DNS domain or host. You can specify multiple RP records for a given DNS domain or host. The record has two parts: an e-mail address in the same DNS format as the one in the SOA resource record, and a DNS domain name that points to additional information about the contact. | |
RT | The route through resource record, which specifies an intermediate host that routes packets to a destination host. The RT record is used in conjunction with the ISDN and X.25 resource records. It is syntactically and semantically similar to the MX record type and is used in much the same way. | |
SOA | The start of authority resource record, which indicates that this DNS server is the authoritative source of information for the data within this DNS domain. The SOA resource record is the first record in each of the DNS database files. It is created automatically by DNS Manager when you create a new DNS zone. | |
TXT | The text resource record, which associates general textual information with an item in the DNS database. A typical use is for identifying a host's location (for example, "Location: Building 26S, Room 2499"). The text string must be less than 256 characters, but you can associate multiple TXT resource records with one item. | |
WINS | A record that contains the IP address of the WINS server configured on this DNS Server for WINS name resolution. A WINS record is automatically created by configuring a zone property for WINS lookup. In other words, it is not created by using the Add Record command in DNS Manager. | |
Table 2.2 DNS Resource Record Types (Continued)
Record type | Description |
WINS_R | A record that instructs Microsoft DNS server to use a NetBIOS node adapter status (nbtstat) command to resolve a DNS client reverse-lookup query. The reverse-lookup query requests the name of a computer identified only by an IP address. A WINS_R record is automatically created by configuring a zone property for WINS reverse lookup. In other words, it is not created by using the Add Record command in DNS Manager. |
WKS | The well-known service resource record, which describes the services provided by a particular protocol for a particular interface. The protocol is usually TCP or User Datagram Protocol (UDP) but can be any of the entries listed in the Protocols file (Systemroot\System32\Drivers\... \Protocol on the drive where your Windows NT Server system files reside). The services described are the services listed below port number 256 in the Services file (\Systemroot\System32\Drivers\...\Services). |
X.25 | The X.25 resource record is a variation of the A resource record. Rather than mapping a host name to an IP address, the X.25 record maps the name to an X.121 address. X.121 is the International Standards Organization (ISO) standard that specifies the format of addresses used in X.25 networks. The X.25 resource record is designed for use in conjunction with the RT resource record. |
All of the resource records listed in the preceding table are commonly used by DNS name servers on the Internet except for the WINS and WINS_R resource records. These records are specifically implemented for interoperability between Microsoft DNS servers and Microsoft WINS servers.
Because these records are unique to Microsoft DNS servers, when transferring primary zone files to a secondary zone, these records should not be copied to a DNS name server running non-Microsoft DNS server software.
If you are using WINS lookup or WINS reverse lookup with a non-Microsoft DNS server, use the following procedure.
Û To prevent copying WINS or WINS_R records to a non-Microsoft DNS server
1. Start DNS Manager.
2. Right-click the folder for the appropriate zone.
3. Click Properties.
4. Click the WINS Lookup or WINS Reverse Lookup tab.
5. Select the Settings only affect local server check box.
6. Click OK.
The remaining sections of this chapter provide information about using the New Host and New Record commands to provide the information that allows remote users to locate your Internet Information Server and Web, FTP, and Gopher services.