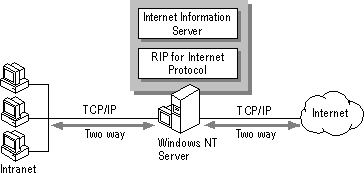
Some organizations need to provide an unrestricted Internet gateway for their users. For example, researchers need to scan the Internet directly as a major part of their work, and then combine information gleaned from the Internet with information that is on the intranet. Each of these users does not need to connect to the Internet through a modem. Instead, one computer running Windows NT Server can serve as a simple gateway to the Internet, as shown in Figure 3.12.

Figure 3.12 A Windows NT–based computer serving as a gateway to the Internet
The computer that serves as a gateway must have:
Internet Information Server can run on the gateway computer, but it is optional.
For information on configuring TCP/IP routing and the RIP for Internet Protocol service, see the Windows NT Server Networking Supplement and Windows NT Server Resource Kit: Windows NT Server Networking Guide.
Routing works both ways. Either traffic can pass in both directions or traffic cannot pass through the server at all. If you enable the RIP for Internet Protocol service, you need to protect all sensitive data on your intranet by other means, such as access control on NTFS drives.
Make sure that the users who have direct Internet access are aware of the security issues. In fact, you should periodically remind them of these issues.
It is most convenient to run Internet Information Server on the computer that serves as the Internet gateway. It is an ideal place for shared directories where Internet users and users of the intranet can deposit and retrieve files, and for indexes of those files.
Also note that Internet users running Windows NT, Windows for Workgroups, LAN Manager, or MS-DOS networking clients can connect to resources on any computer connected to the Internet by issuing net use commands. An Internet user running Windows NT, Windows for Workgroups, LAN Manager, or an MS-DOS networking client can issue a net view command and then see a list of your corporate servers. Standard Windows NT security controls this method of access.
For more information about Windows NT security, see Windows NT Server Concepts and Planning, the Internet Information Server Installation and Administration Guide, and the Microsoft Windows NT Resource Kit: Windows NT Server Resource Guide.