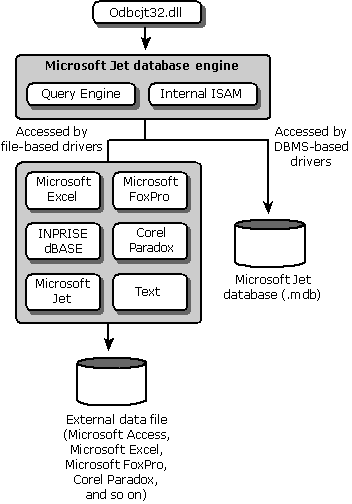
Driver writers must be aware that the driver architecture can affect whether an application can use DBMS-specific SQL.

When the driver accesses the physical data directly, the driver acts as both driver and data source. The driver must process both ODBC calls and SQL statements. Developers of file-based drivers must write their own database engines.
When a separate database engine is used to access physical data, the driver processes only ODBC calls. It passes SQL statements to the database engine for processing.
File and DBMS ODBC configurations can exist on a single network.
When a driver is required to work with a variety of data sources, it can be used as middleware. Heterogeneous join engine architecture can make the driver appear as a driver manager. Drivers can also be installed on servers, where they can be shared by a series of clients.
It is preferable to install the redistributable files for ODBC components using the self-contained setup included with the Microsoft® Data Access Components (MDAC) SDK. Updates to this setup are available on the Microsoft Universal Data Access Web site. After downloading any updates to the executable file, extract the files from Mdac_typ.exe in the \Redist directory.
To run the command, click Start, click Run, and then type mdac_typ.exe /C /T:<path_to_dir>, where <path_to_dir> is the target directory for the extracted files.
For more information about driver architecture, see Driver Architecture in Chapter 3 of the ODBC Programmer's Reference, "ODBC Architecture."
More information about driver issues can be found in the locations described in the following table.
| Issue | Topic | Location |
| Compatibility issues with applications and drivers | Application/Driver Compatibility | Chapter 17, "Programming Considerations," in the ODBC Programmer's Reference |
| Writing ODBC drivers | Writing ODBC 3.x Drivers | Chapter 17, "Programming Considerations," in the ODBC Programmer's Reference |
| Driver guidelines for backward compatibility | Driver Guidelines for Backward Compatibility | Appendix G, "Driver Guidelines for Backward Compatibility," in the ODBC Programmer's Reference |
| Connecting to a driver | Choosing a Data Source or Driver | Chapter 6, "Connecting to a Data Source or Driver," in the ODBC Programmer's Reference |
| Identifying drivers | Viewing Drivers | "Viewing Drivers," accessed from the Microsoft ODBC Data Source Administrator online help file |
| Enabling connection pooling | ODBC Connection Pooling | Chapter 6, "ODBC Connection Pooling," in the ODBC Programmer's Reference |
| Unicode/ANSI driver and connection issues | Unicode Drivers | Chapter 17, "Programming Considerations," in the ODBC Programmer's Reference |