| Microsoft Office 2000 Developer | |
Almost any application uses strings that contain variables in some form or another; you dimension a variable, assign a value to it, and output that variable as part of a string. If you need to output a string that contains multiple variables, it can often be a painstaking process adding all of the quote characters and concatenation operators in the right places.
For example, the following code contains several string variables:
Dim Fname As String, Lname As String
Dim varAge As Variant, varDate as Variant
Fname = "John"
Lname = "Doe"
varAge = 42
varDate = "August 15"
TextBox1.Text = Fname & Lname & " will be " & varAge & _
" old on " & varDate & " of this year."
In the preceding example, it would be easy to leave out a quotation mark character or space or to misplace a concatenation character. The result would be a compile-time error, and finding your mistake could prove especially difficult in a long string.
The String Editor add-in, included in Office 2000 developer, greatly simplifies the process of formatting complex strings such as SQL statements or scripts. Using the String Editor, you can simply enter your string as straight text, then mark any string variables within the string. On completion, the String Editor will automatically format the string for you, inserting all of the necessary quotes and other formatting characters.
To insert a formatted string into your code
Note The String Editor menu item is only available when the VBA String Editor add-in is loaded. For information about loading add-ins, see Accessing Office 2000 Developer Tools.
Fname Lname will be varAge old on varDate of this year.
Each selection will be marked as a variable and color-coded blue in the String Editor.
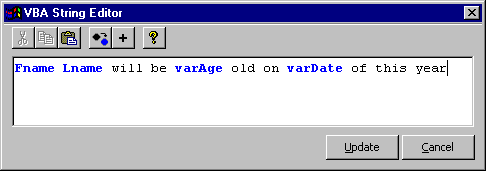
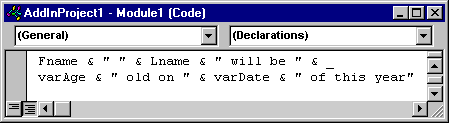
The following table shows some examples of the formatting applied by the String Editor.
| In the String Editor | Resulting code |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|