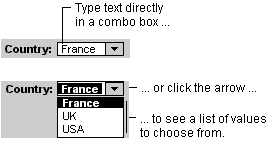
In many cases, it's quicker and easier to select a value from a list than to remember a value to type. With a combo box, you can do either without using too much space on a form. A combo box is like a text box and a list box combined.

When you enter text or select a value in a combo box, if the combo box is bound, the entered or selected value is inserted into the field that the combo box is bound to.
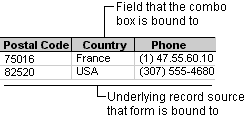
The list in a combo box consists of rows of data. Rows can have one or more columns, which can appear with or without headings. If a multiple-column combo box is bound, Microsoft Access stores the values from one of the columns.
You can use an unbound combo box to store a value that you can use with another control. For example, you could use an unbound combo box to limit the values in another combo box or in a custom dialog box. You could also use an unbound combo box to find a record based on the value you select in the combo box.
Combo boxes have a LimitToList property that you can use to control whether any value can be entered in the list, or only text that matches one of the values in the list can be entered.
If you have room on your form and you want a list to appear at all times, or if you always want to limit data entries to values in the list, you might want to use a list box instead of a combo box. For more information on list boxes, click  .
.