Certain relationships can provide a name by which the origin object refers to the destination object. Such a relationship is called a naming relationship. A collection of naming relationships is a naming collection.
Certain naming collections require that all destination objects in the collection have unique names. Such a collection is referred to as a unique-naming collection.
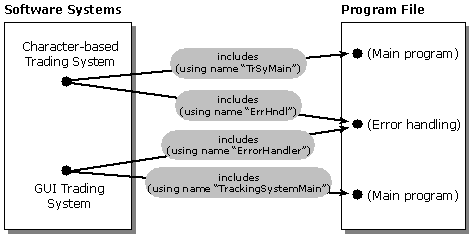
Some information models require that an object can have multiple names. For example, consider a system in which a single program can have two different file names, because there are two different file systems that allow and disallow long names, respectively. The following figure illustrates.

The figure shows four relationships. Each relationship specifies a name by which one of the objects (the origin object) refers to the other object (the destination object). In particular, notice that the object representing the error-handling program file has two different names, "ErrHndl" and "ErrorHandler".
In order to support this kind of capability, the Type Information Model attaches the name property to the relationship type, not to the object class. This enables an object to have as many names as it has relationships (that is, relationships for which it is the destination).