 To install the Microsoft Network Monitor Agent on a single computer
To install the Microsoft Network Monitor Agent on a single computer
This section describes the following tools for monitoring your network:
The Windows 98 compact disc includes a protocol driver and an agent for Microsoft Network Monitor. The protocol driver provides performance counters that can be viewed by using System Monitor if you want to assess certain network traffic statistics for network driver interface specification (NDIS) version 5.0 protected-mode network adapters. The Network Monitor Agent, which runs as a Windows 98 service, works with the protocol driver for use with the Microsoft Network Monitor application. You can use this application to detect and troubleshoot problems on LANs, WANs, and Microsoft Remote Access Service (RAS) connections.
Note
The Network Monitor application is provided with Microsoft Systems Management Server, a client-server system that allows administrators to perform key management functions for distributed computers from a central location.
When you install the Network Monitor Agent, the protocol driver is also installed automatically. You must have both the agent and the driver installed if you want to use the agent with Network Monitor to conduct remote captures of network traffic to and from a computer running Windows 98.
However, if you want only to view the performance counters in System Monitor and you want to prevent anyone from gaining access to the local computer by way of the Network Monitor Agent, you can choose to install only the protocol driver.
Note
The Network Monitor application uses NetBIOS to control the remote-capture computer. If you are using the IPX/SPX-compatible protocol to connect the agent and manager computers, you must enable NetBIOS support for IPX/SPX.
 To install the Microsoft Network Monitor Agent on a single computer
To install the Microsoft Network Monitor Agent on a single computer
 To install only the Microsoft Network Monitor protocol driver
To install only the Microsoft Network Monitor protocol driver
You can run Network Monitor Agent as a service, or you can start and stop the agent as an executable application.
 To start Microsoft Network Monitor Agent
To start Microsoft Network Monitor Agent
Network Monitor Agent is removed from the system each time you log off and must be restarted for each user who logs on if the agent is not scheduled to run as a service.
 To run Network Monitor Agent as a service
To run Network Monitor Agent as a service
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\RunServices
If Network Monitor Agent has been started as a service, it continues to run after a user logs off. You can, however, type a command to stop running the agent, whether the agent was started as a service or run from the command prompt.
 To stop Microsoft Network Monitor Agent
To stop Microsoft Network Monitor Agent
You can configure options for Network Monitor by defining properties for the Network Monitor protocol driver.
 To configure the Microsoft Network Monitor protocol driver
To configure the Microsoft Network Monitor protocol driver
You can also define a description for each network adapter in this dialog box, so that the administrator running the Network Monitor application can determine which adapter to select.
This additional information, which is similar to a comment, is not updated or changed if another user logs on to this computer.
For networks that use Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) for system management, Windows 98 includes an SNMP Agent that conforms to the SNMP version 1 specification. This agent allows you to monitor, from an SNMP console, remote connections to computers running Windows 98. After this agent has been installed, you do not need to make any other modifications to client computers to use SNMP.
The SNMP Agent is implemented as a Win32-based service and works using Windows Sockets over both TCP/IP and IPX/SPX. The extension agents are implemented as Win32 dynamic-link libraries (DLLs). (For more information about writing SNMP management information bases [MIBs] under Windows 98, see the Microsoft Windows Platform Software Development Kit.) The configuration information for the RFC 1156 extension agent is placed in the registry under the following key:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\System\CurrentControlSet\Services\SNMP\Parameters
 To install Microsoft SNMP Agent
To install Microsoft SNMP Agent
If you are prompted to specify the location of additional files, specify the path to the Windows 98 source files on a shared network directory or on the Windows 98 compact disc.
Use System Policy Editor to set the following policies for the computer:
| Policy | Description |
|---|---|
| Communities | Specifies one or more groups of hosts to which this computer belongs for purposes of administration using the SNMP service. These are the communities allowed to query the SNMP Agent. |
| Permitted Managers | Specifies Internet Protocol (IP) or Internetwork Packet Exchange (IPX) addresses allowed to obtain information from an SNMP Agent. If this policy is not selected, any SNMP console can query the agent. |
| Traps for Public Community | Specifies trap destinations, or IP or IPX addresses of hosts in the public community to which you want the SNMP service to send traps. |
| Internet MIB (RFC 1156) | Allows you to specify the contact name and location if you are using Internet MIB. |
If you want to configure the Windows 98 SNMP Agent to send traps to a community other than the public community, you must either edit the registry directly or add a new system policy.
 To add SNMP communities by editing the registry
To add SNMP communities by editing the registry
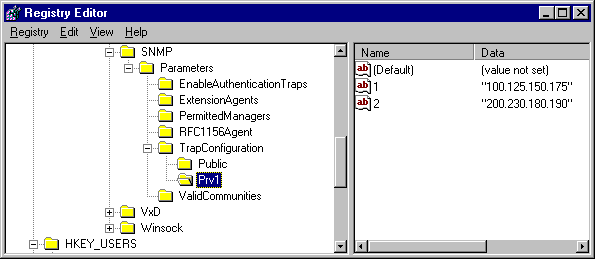
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\System\CurrentControlSet\Services\SNMP\Parameters\TrapConfiguration
The following screen shows an example of what the registry should look like after adding a new community named Prv1.
 To add SNMP communities by using system policies
To add SNMP communities by using system policies
The following shows the complete syntax for this entry:
POLICY "Name Of New Policy" KEYNAME System\CurrentControlSet\Services\SNMP\Parameters \TrapConfiguration\Name Of New CommunityPART !!Traps_PublicListbox LISTBOX VALUEPREFIX "" END PART END POLICY
Note
The registry key and value names are case-sensitive. Also, the registry key name (System\...\Name Of New Community) must be one continuous line in the Windows.adm file.
For example, the following adds a policy for a community named Prv1:
POLICY "Traps for Prv1 Community"
KEYNAME
System\CurrentControlSet\Services\SNMP\Parameters\TrapConfiguration\Prv1
PART !!Traps_PublicListbox LISTBOX
VALUEPREFIX ""
END PART
END POLICY
After editing and saving Windows.adm, you can see this new policy by running System Policy Editor and selecting the Computer policy under Network named SNMP. You can use this policy exactly as you would use the policy named Traps for Public Community.