Previous | Next
Overview of Windows 98 Architecture Components
Microsoft Windows 98 is a 32-bit operating system that provides built-in Internet connectivity, Plug and Play hardware support, high performance, robustness, and backward compatibility with Windows 95. Windows 98 enhancements to Windows 95 include more sophisticated power management, multiple video display support, and integrated support for the latest hardware. Also included is support for the new Win32 Driver Model (WDM), allowing a WDM device to run under both Windows 98 and future versions of Windows NT using the same driver.
These features are supported by the components shown in Figure 28.1.
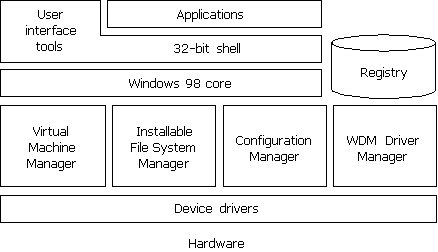
Figure 28.1 Windows 98 components
Like Windows 95, Windows 98 is derived from the Windows 3.1 platform and includes the following features:
-
A complete 32-bit kernel, including memory management, and preemptive multitasking and multithreading support.
-
A fully integrated 32-bit, protected-mode file system, which eliminates the need to rely on a separate copy of MS-DOS once the system boots up.
-
32-bit installable file system drivers supporting FAT, FAT32, ISO 9660 (CD-ROM), ISO 13346 (Universal Disk Format/Digital Video Disc [UDF/DVD]), network redirection, and high performance. These file system drivers also support the use of long file names and an open, modular architecture to handle future expansion.
-
WDM support, which allows a WDM-supported device to run under both Windows 98 and future versions of Windows NT using the same driver.
-
Improved system-wide robustness and "cleanup" after an application or driver fails. This delivers a more stable and reliable operating environment.
-
A dynamic hardware and environment configuration, which reduces the need for users to adjust and restart their systems manually.
This chapter describes the key components that make up the Windows 98 architecture, beginning with its central information store, the registry, and proceeding from bottom to top.

