Microsoft Windows 98 includes support for Transport Control Protocol/Internet Protocol (TCP/IP), Internetwork Packet Exchange/Sequenced Packet Exchange (IPX/SPX) – compatible protocols, and NetBEUI. The following sections describe how support for each type of protocol is implemented in Windows 98.
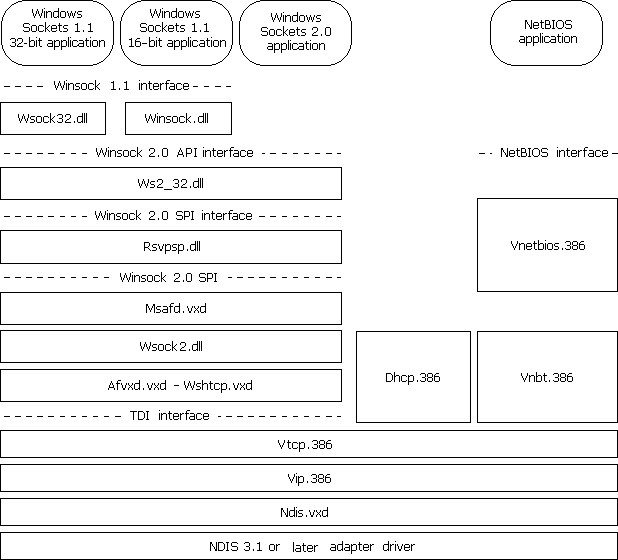
TCP/IP is a popular routable protocol for wide-area networks (WANs). The TCP/IP module, Vtcp.vxd, is accessible through the Windows Sockets interface or through the NetBIOS interface. For information about Windows Sockets and interprocess communication mechanisms, see "Architecture for Interprocess Communications" later in this chapter.
Figure 29.12 shows the TCP/IP architecture.

Figure 29.12 Windows 98 architecture for Microsoft TCP/IP
The Microsoft IPX/SPX-compatible protocol uses the Nwnblink.vxd module to support NetBIOS over IPX and to support the NetBIOS programming interface. Figure 29.13 shows the architecture for the IPX/SPX-compatible protocol.
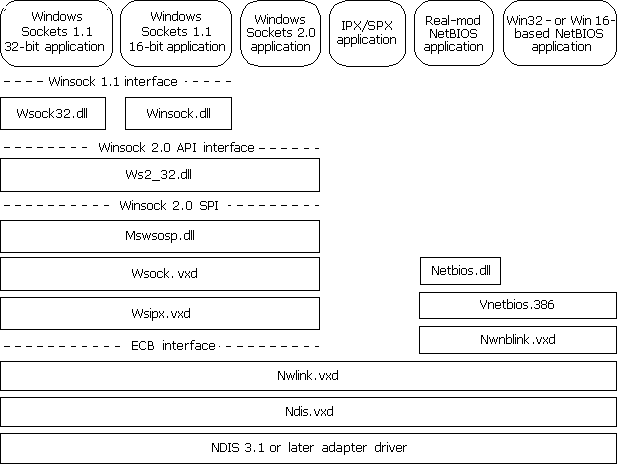
Figure 29.13 Windows 98 architecture for IPX/SPX-compatible protocol
The Microsoft IPX/SPX-compatible protocol is compliant with NDIS 3.1 and later and enables computers running Windows 98 to communicate over a routable IPX-compatible protocol. This protocol can use Novell NetWare servers configured as routers (as well as other IPX routers) to transfer its packets across LANs to access resources on other computers running Windows 98.
As Figure 29.14 shows, the NetBEUI module, Netbeui.vxd, implements the NetBIOS framing protocol.
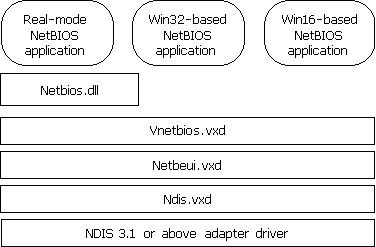
Figure 29.14 Windows 98 architecture for NetBEUI protocol