B.2. LFSR Checksum Functions
The checksum algorithm uses the same LFSR as is used in the initiation key process.
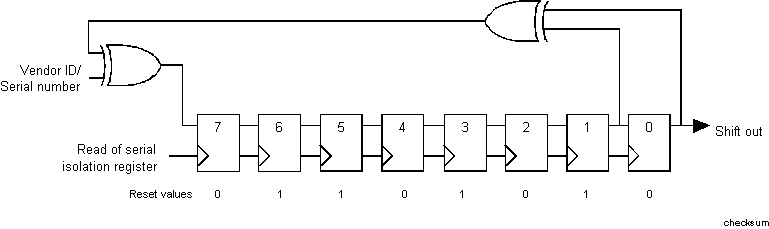 Figure B-2. Checksum LFSR
The LFSR resets to 0x6A upon receiving the Wake[CSN] command. The next shift value for the LFSR is calculated as LFSR[1] XOR LFSR[0] XOR Serial Data. The LFSR is shifted right one bit at the conclusion of each pair of reads to the Serial Isolation register. LFSR[7] is assigned the next shift value described above.
As an example of the data pattern generated by the LFSR during the serial shift protocol consider a card with a vendor abbreviation of "PXQ", a manufacturer-specific product number of 540, a revision level of "9", and a serial number of 0x04000100.
The ASCII EISA ID for "PXQ" is 0x1143 where 0x43 is byte 0 and 0x11 is byte 1 as per Table 2, Section 6.1.
Figure B-2. Checksum LFSR
The LFSR resets to 0x6A upon receiving the Wake[CSN] command. The next shift value for the LFSR is calculated as LFSR[1] XOR LFSR[0] XOR Serial Data. The LFSR is shifted right one bit at the conclusion of each pair of reads to the Serial Isolation register. LFSR[7] is assigned the next shift value described above.
As an example of the data pattern generated by the LFSR during the serial shift protocol consider a card with a vendor abbreviation of "PXQ", a manufacturer-specific product number of 540, a revision level of "9", and a serial number of 0x04000100.
The ASCII EISA ID for "PXQ" is 0x1143 where 0x43 is byte 0 and 0x11 is byte 1 as per Table 2, Section 6.1.
| Vendor ID Byte 0: | 0x43 |
| Vendor ID Byte 1: | 0x11 |
| Vendor ID Byte 2: | 0x54 |
| Vendor ID Byte 3: | 0x09 |
| Serial Number Byte 0: | 0x00 |
| Serial Number Byte 1: | 0x01 |
| Serial Number Byte 2: | 0x00 |
| Serial Number Byte 3: | 0x04 |
The serial identifier is sent as
0x43 (Bit 0 to bit 7, 1 1 0 0 0 0 1 0)
0x11 1 0 0 0 1 0 0 0
0x54 0 0 1 0 1 0 1 0
0x09 1 0 0 1 0 0 0 0
0x00 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0x01 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0x00 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0x04 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0
The LFSR is reset to value 0x6A when this card receives a Wake[CSN] command. After 64 pairs of reads of the Serial Isolation register, the LFSR will have the value 0xDC.
 Figure B-2. Checksum LFSR
The LFSR resets to 0x6A upon receiving the Wake[CSN] command. The next shift value for the LFSR is calculated as LFSR[1] XOR LFSR[0] XOR Serial Data. The LFSR is shifted right one bit at the conclusion of each pair of reads to the Serial Isolation register. LFSR[7] is assigned the next shift value described above.
As an example of the data pattern generated by the LFSR during the serial shift protocol consider a card with a vendor abbreviation of "PXQ", a manufacturer-specific product number of 540, a revision level of "9", and a serial number of 0x04000100.
The ASCII EISA ID for "PXQ" is 0x1143 where 0x43 is byte 0 and 0x11 is byte 1 as per Table 2, Section 6.1.
Figure B-2. Checksum LFSR
The LFSR resets to 0x6A upon receiving the Wake[CSN] command. The next shift value for the LFSR is calculated as LFSR[1] XOR LFSR[0] XOR Serial Data. The LFSR is shifted right one bit at the conclusion of each pair of reads to the Serial Isolation register. LFSR[7] is assigned the next shift value described above.
As an example of the data pattern generated by the LFSR during the serial shift protocol consider a card with a vendor abbreviation of "PXQ", a manufacturer-specific product number of 540, a revision level of "9", and a serial number of 0x04000100.
The ASCII EISA ID for "PXQ" is 0x1143 where 0x43 is byte 0 and 0x11 is byte 1 as per Table 2, Section 6.1.