7.2. Motherboard SCSI Design Alternative
The motherboard SCSI alternative for the internal, external and mixed configurations is shown in figure 3.
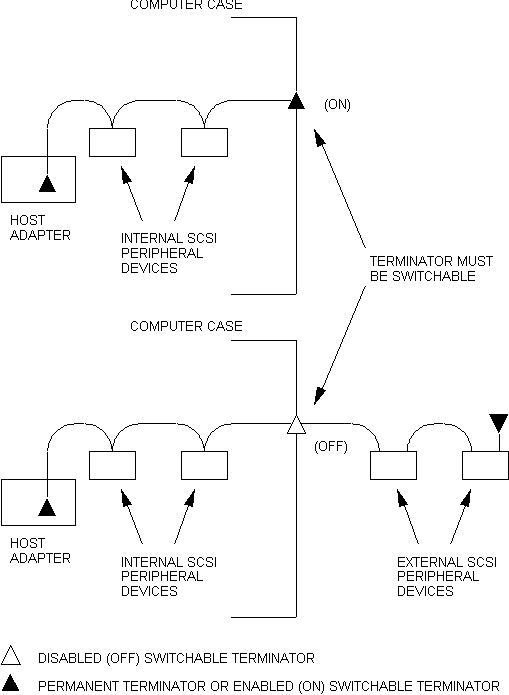 Figure 3 - Motherboard SCSI Design
In the internal configuration the host adapter and internal terminator supply the necessary termination.
The internal SCSI bus is routed as necessary within the PC, complying to the rules in SPI, to one or more SCSI devices. The end of the internal SCSI bus ends with an internal terminator.
If cables are employed, keyed connectors are required on the motherboard and the cables to ensure that the cable is plugged in correctly (not reversed or shifted). Systems with backplane SCSI buses are required to meet the electrical requirements of the SCSI-3 Parallel Interface document, particularly with respect to characteristic impedance.
In the external configuration the internal and external terminator supply the necessary termination.
Peripheral subsystems are required to provide two 50-position high-density shielded connectors on the enclosure. The SCSI bus internal to the enclosure is routed from one external SCSI connector to the SCSI device(s) within the enclosure and then to the second external SCSI device connector.
One external terminator must be installed on the last SCSI peripheral subsystem. The user may purchase the external terminator and cable when installing the first SCSI peripheral subsystem.
In systems that support mixed configurations, the exit-point terminator is automatically enabled or disabled to correctly terminate the SCSI bus. This is accomplished through mechanical or electronic detection of the attached cable or electronic detection of attached SCSI device(s).
Figure 3 - Motherboard SCSI Design
In the internal configuration the host adapter and internal terminator supply the necessary termination.
The internal SCSI bus is routed as necessary within the PC, complying to the rules in SPI, to one or more SCSI devices. The end of the internal SCSI bus ends with an internal terminator.
If cables are employed, keyed connectors are required on the motherboard and the cables to ensure that the cable is plugged in correctly (not reversed or shifted). Systems with backplane SCSI buses are required to meet the electrical requirements of the SCSI-3 Parallel Interface document, particularly with respect to characteristic impedance.
In the external configuration the internal and external terminator supply the necessary termination.
Peripheral subsystems are required to provide two 50-position high-density shielded connectors on the enclosure. The SCSI bus internal to the enclosure is routed from one external SCSI connector to the SCSI device(s) within the enclosure and then to the second external SCSI device connector.
One external terminator must be installed on the last SCSI peripheral subsystem. The user may purchase the external terminator and cable when installing the first SCSI peripheral subsystem.
In systems that support mixed configurations, the exit-point terminator is automatically enabled or disabled to correctly terminate the SCSI bus. This is accomplished through mechanical or electronic detection of the attached cable or electronic detection of attached SCSI device(s).
 Figure 3 - Motherboard SCSI Design
In the internal configuration the host adapter and internal terminator supply the necessary termination.
The internal SCSI bus is routed as necessary within the PC, complying to the rules in SPI, to one or more SCSI devices. The end of the internal SCSI bus ends with an internal terminator.
If cables are employed, keyed connectors are required on the motherboard and the cables to ensure that the cable is plugged in correctly (not reversed or shifted). Systems with backplane SCSI buses are required to meet the electrical requirements of the SCSI-3 Parallel Interface document, particularly with respect to characteristic impedance.
In the external configuration the internal and external terminator supply the necessary termination.
Peripheral subsystems are required to provide two 50-position high-density shielded connectors on the enclosure. The SCSI bus internal to the enclosure is routed from one external SCSI connector to the SCSI device(s) within the enclosure and then to the second external SCSI device connector.
One external terminator must be installed on the last SCSI peripheral subsystem. The user may purchase the external terminator and cable when installing the first SCSI peripheral subsystem.
In systems that support mixed configurations, the exit-point terminator is automatically enabled or disabled to correctly terminate the SCSI bus. This is accomplished through mechanical or electronic detection of the attached cable or electronic detection of attached SCSI device(s).
Figure 3 - Motherboard SCSI Design
In the internal configuration the host adapter and internal terminator supply the necessary termination.
The internal SCSI bus is routed as necessary within the PC, complying to the rules in SPI, to one or more SCSI devices. The end of the internal SCSI bus ends with an internal terminator.
If cables are employed, keyed connectors are required on the motherboard and the cables to ensure that the cable is plugged in correctly (not reversed or shifted). Systems with backplane SCSI buses are required to meet the electrical requirements of the SCSI-3 Parallel Interface document, particularly with respect to characteristic impedance.
In the external configuration the internal and external terminator supply the necessary termination.
Peripheral subsystems are required to provide two 50-position high-density shielded connectors on the enclosure. The SCSI bus internal to the enclosure is routed from one external SCSI connector to the SCSI device(s) within the enclosure and then to the second external SCSI device connector.
One external terminator must be installed on the last SCSI peripheral subsystem. The user may purchase the external terminator and cable when installing the first SCSI peripheral subsystem.
In systems that support mixed configurations, the exit-point terminator is automatically enabled or disabled to correctly terminate the SCSI bus. This is accomplished through mechanical or electronic detection of the attached cable or electronic detection of attached SCSI device(s).