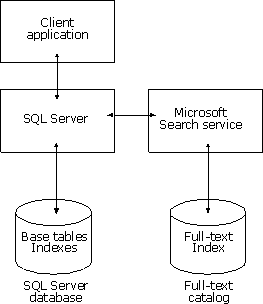
The Microsoft Search service is a full-text indexing and search engine.
Earlier versions of Microsoft® SQL Server™ supported only basic character search capabilities:
These searches could be performed only against char and varchar columns in a database, although the PATINDEX function could be used to find the location of a string in a column having a text data type.
Using the Microsoft Search service allows SQL Server version 7.0 to support more sophisticated searches on character string columns.
The Microsoft Search service has two roles:
Implements the full-text catalogs and indexes defined for a database. Accepts definitions of full-text catalogs, and the tables and columns making up the indexes in each catalog. Implements requests to populate the full-text indexes.
Processes full-text search queries. Determines which entries in the index meet the full-text selection criteria. For each entry that meets the selection criteria, it returns the identity of the row plus a ranking value to the MSSQLServer service, where this information is used to construct the query result set. The types of queries supported include searching for:
The full-text engine runs as a service named Microsoft Search on Microsoft Windows NT®. It is installed when the Full-Text Search feature is selected during custom installation. The Microsoft Search service itself is not installed on Microsoft Windows® 95/98 or Windows NT Workstation, although Windows 95/98 clients and Windows NT Workstation clients can make use of the service when connected to a SQL Server installation running on Windows NT Server.
The Microsoft Search service runs in the context of the local system account. During setup, SQL Server adds itself as an administrator of the Microsoft Search service. To ensure this relationship is maintained correctly, all changes to the MSSQLServer service account information must be made using the Properties tab of the SQL Server Properties dialog box in SQL Server Enterprise Manager.
The full-text catalogs and indexes are not stored in a SQL Server database. They are stored in separate files managed by the Microsoft Search service. The full-text catalog files are accessible only to the Microsoft Search service and the Windows NT system administrator.

| Full-text Query Architecture | Full-text Catalogs and Indexes |