Steve Kirk
Microsoft Developer Network
May 1998
Summary: Details the Duwamish Books database schema. (10 printed pages) Knowledge of Microsoft Access and general relational database design will be helpful. Includes:
This article describes the database used in Phase 1 of the Duwamish Books sample application. For an introduction to and an outline of the four phases of the Duwamish Books sample, see Robert Coleridge's "An Introduction to the Duwamish Books Sample."
As in the Phase 1 applications, the database design emphasizes simple practicality rather than technical purity. The design captures the business entities and processes of the bookstore but leaves some scalability issues to be addressed in subsequent phases.
In this design related tables provide for some data size efficiencies, but the importance of having a normalized design, where each entity contains only data that is unique to itself, is secondary to overall simplicity. The model will be revised in subsequent sample phases to support business growth to multiple locations and more activity.
The Microsoft® Access 98 .mdb database provides an appropriately scaled data repository for the desktop applications that are comprised in this phase of the sample. The complete data model, with table definitions, referential integrity specifications, and a set of sample data, is included in duwamish.mdb.
Statements of the business transactions to be modeled provide a starting point for the data model. The nouns in these statements can be thought of as data and the verbs as the processes that operate upon data. The nouns are developed into data entities with attributes that describe the entities and the relationships between entities. This suite of statements represents the primary business processes of the bookstore with the emphasized nouns and verbs forming the basic data model. Words used as NOUNs are in all caps and those used as VERBs are in italic caps.
Many words in these statements can be used as nouns or verbs. For instance, SEARCH is used as a verb because no record of a search is ever saved. ORDER, however, is used as a noun because an order is saved as a data entity.
CUSTOMER or EMPLOYEE SEARCHES for ITEMs
An ITEM usually describes a book title that is available through the store, but it may also represent a related merchandise type. Each type of merchandise carried is modeled by an ITEM.
EMPLOYEE PLACES ORDER for ITEMs with SUPPLIER
The purchase ORDER is to a single SUPPLIER and contains one or more ORDER_DETAILs. An ORDER_DETAIL contains an ITEM and a quantity.
EMPLOYEE RECEIVES ORDER of ITEMs from SUPPLIER
The data model represents the flow of merchandise through the store to provide a rich historical data source for analysis. Although a simple attribute of quantity on hand could be added to each ITEM, this doesn't capture inventory behavior over time. Receiving an ORDER changes the status of the ORDER and generates one or more INVENTORY_TRANSACTIONs. An INVENTORY_TRANSACTION contains an ITEM and quantity and, in the case of receiving, the corresponding ORDER_DETAIL.
CUSTOMER PLACES ORDER for ITEMs with STORE
The sale ORDER contains one or more ORDER_DETAILs. A sale ORDER is used for special order ITEMs or when merchandise is to be shipped.
CUSTOMER PURCHASES ITEMs at cash register
This generates a SALE and usually generates INVENTORY_TRANSACTIONs for the ITEMs that the CUSTOMER takes away.
STORE SHIPS ORDER ITEMs to CUSTOMER
This generates a SALE and SALE DETAILs or fulfills a previously generated SALE. It also generates INVENTORY TRANSACTIONs for the ITEMs shipped.
In the following section, the nouns are developed into data. The verbs drop out of the data model to become specifications for code within the applications that act on the data model. Field specifications include data type and also specify index rules and relationships between entities.
The Item group consists of the Item entity and the related entities that complete the item description. An item entity exists for each item carried in the store, and searches are performed against the Items table.
Item Entity
| Field name | Data type | Field attributes and relationships | Description |
| PKId | AutoNumber | Primary key | |
| ItemTypeId | Long | Foreign key to ItemType table (Enforced reference) | Item type (all items) |
| AuthorId | Long | Foreign key to author in Authors table (optional) | Book author (books) |
| PublisherId | Long | Foreign key to publisher in Contacts table (optional) | Book publisher (books) |
| SupplierId | Long | Foreign key to supplier in Contacts table (Enforced reference) | Item supplier (all items) |
| TaxRateId | Long | Foreign key to TaxRate table (Enforced reference) | Tax rate for item |
| InStock | Integer | Quantity of item in stock | |
| ReorderLevel | Integer | Stock level to trigger reorder | |
| PublicationDate | Integer | Year of publication (books) | |
| ISBN | Text(50) | ISBN (books). Model or supplier stock number (non-books) | |
| ImageFileSpec | Text(255) | Filespec of relevant image | |
| Title | Text(50) | Title of book (books) | |
| Description | Text(255) | Description of item (for example, fiction or nonfiction)
(see normalization comments) |
|
| UnitPrice | Currency | Price of item | |
| KeyWords | Text(255) | Set of key words (see normalization comments) |
ItemType Entity
| Field name | Data type | Field attributes and relationships | Description |
| PKId | AutoNumber | Primary key | |
| Code | Text(12) | Code of type | |
| Description | Text(50) | Description | |
| IsBook | Yes/No | Yes indicates that item type is a book |
Author Entity
| Field name | Data type | Field attributes and relationships | Description |
| PKId | AutoNumber | Primary key | Uniquely identifies author |
| LastName | Text(50) | Author's last name | |
| FirstName | Text(50) | Author's first name |
TaxRate Entity
| Field name | Data type | Field attributes and relationships | Description |
| PKId | AutoNumber | Primary key | |
| Description | Text(50) | Description | |
| TaxRate | Number | Tax rate |
Orders represent an intention to buy or sell. An employee places a purchase order with a supplier. Customers place Sales orders. An order consists of a single order entity and at least one order detail entity.
Order Entity
| Field name | Data type | Field attributes and relationships | Description |
| PKId | AutoNumber | Primary key | |
| CustomerId | Long | Refers to customer in Customers table | References order customer (for sales orders) |
| EmployeeId | Long | Foreign key to Employees table (Enforced reference) | References order employee (for purchase orders) |
| SupplierId | Long | Foreign key to supplier in Contacts table (optional) | References order supplier (for purchase orders) |
| OrderDate | Date/Time | Date order is placed | |
| PickupDate | Date/Time | Date order was picked up | |
| Status | Text | Note space for status options. The following values are defined by the system:
'ENTERED', (P/S) 'ORDERED', (P) 'READY', (S) 'RECEIVED', (P) 'SHIPPED', (S) 'WILLCALL', (S) 'COMPLETED', (P/S) (see normalization comments) |
|
| SubTotal | Currency | Amount from order details | |
| ShippingHandling | Currency | Shipping and handling amount | |
| Tax | Currency | Tax amount | |
| Total | Currency | Total order amount | |
| IsSales | Yes/No | Yes indicates that order is a sales order; No indicates that order is a purchase order. | |
| ShipToName | Text(50) | Name on address label | |
| ShipToAddress1 | Text(50) | Address label line 1 | |
| ShipToAddress2 | Text(50) | Address label line 2 | |
| ShipToCity | Text(50) | City on address label | |
| ShipToState | Text(2) | State on address label | |
| ShipToZipCode | Text(10) | Zip code on address label | |
| ShipToPhone | Text(50) | Phone number for shipping |
OrderDetail Entity
| Field name | Data type | Field attributes and relationships | Description |
| PKId | AutoNumber | Primary key | |
| OrderId | Long | Foreign key to Orders table (Enforced reference) | References order |
| ItemId | Long | Foreign key to Items table (Enforced reference) | References item |
| UnitPrice | Currency | Price for each unit | |
| Quantity | Long | Number of units ordered |
A sale represents a transfer of items to a customer. A sale consists of a sale entity and at least one sale detail entity.
Sale Entity
| Field name | Data type | Field attributes and relationships | Description |
| PKId | AutoNumber | Primary key | |
| CustomerId | Long | Foreign key to Customers table (Enforced reference) | References sale customer |
| OrderId | Long | Foreign key to orderin Orders table (optional) | References order |
| EmployeeId | Long | Foreign key to Employees table (Enforced reference) | References employee |
| SaleDate | Date/Time | Date/time of sale | |
| SubTotal | Currency | Subtotal of item sale | |
| Tax | Currency | Tax on item sale | |
| PaymentType | Text(50) | Payment type (for example, cash, check, or credit card) | |
| CreditCardNo | Text(50) | Credit card number | |
| ExpirationDate | Date/Time | Expiration date on credit card | |
| NameOnCard | Text(50) | Name of card holder | |
| Ship | Yes/No | Yes indicates that order will be shipped |
SaleDetail Entity
| Field name | Data type | Field attributes and relationships | Description |
| PKId | AutoNumber | Primary key | |
| SaleId | Long | Foreign key to Sales table (Enforced reference) | References sale |
| ItemId | Long | Foreign key to Items table (Enforced reference) | References item |
| UnitPrice | Currency | Price for each unit | |
| Quantity | Long | Number of units ordered |
The inventory tracking group consists of the InventoryTracking entity. Inventory tracking transactions are entered whenever store inventory changes. Causes of inventory changes are: receiving items from a supplier, selling items to a customer, or administrative sales transactions to account for items removed due to damage or theft.
Inventory Tracking Entity
| Field name | Data type | Field attributes and relationships | Description |
| PKId | AutoNumber | Primary key | |
| ItemID | Long | Foreign key to Items table (Enforced reference) | Identifies item type |
| TransactionId | Long | Refers to orderdetail in OrderDetails table or SaleDetail in SaleDetails table | References order detail or sales detail that generates inventory transaction |
| IsSale | Yes/No | Yes if generator is a sale; No if generator is an order (determines TransactionId reference table). | |
| Quantity | Long | Change to inventory. Positive value indicates receive; negative ship or sales. | |
| TransactionDate | Date/Time | Date of transaction | |
| Notes | Text(255) | Notes on transaction
(see normalization comments) |
The Actors group contains entities that represent people or organizations. The contact entity can represent multiple types of actors, such as publishers and suppliers.
Contact Entity
| Field name | Data type | Field attributes and relationships | Description |
| PKId | AutoNumber | Primary key | |
| ContactType | Text(12) | Contact type. The system defines the following values:
'SUPPLIER', 'PUBLISHER' (see normalization comments) |
|
| LastName | Text(50) | Last name or Company name | |
| FirstName | Text(50) | First name | |
| Address1 | Text(50) | Address line 1 | |
| Address2 | Text(50) | Address line 2 | |
| City | Text(50) | City | |
| State | Text(2) | State | |
| ZipCode | Text(10) | Zip Code | |
| ContactPerson | Text(50) | Person of contact | |
| PhoneNumber | Text(50) | Phone of contact | |
| LastContact | Date/Time | Date of last contact |
Customer Entity
| Field name | Data type | Field attributes and relationships | Description |
| PKId | AutoNumber | Primary key | |
| NickName | Text(50) | Quick identifier | |
| LastName | Text(50) | Last name of customer | |
| FirstName | Text(50) | First name of customer | |
| Address1 | Text(50) | Address line 1 | |
| Address2 | Text(50) | Address line 2 | |
| City | Text(50) | City | |
| State | Text(2) | State | |
| ZipCode | Text(10) | Zip Code | |
| PhoneNumber | Text(50) | Customer's phone number | |
| LastSale | Date/Time | Date of last sale | |
| TotalSaleYTD | Currency | Customer purchase total to date |
Employee Entity
| Field name | Data type | Field attributes and relationships | Description |
| PKId | AutoNumber | Primary key | |
| Alias | Text(50) | Unique | Identifies user |
| LastName | Text(50) | Last name | |
| FirstName | Text(50) | First name | |
| MI | Text(1) | Middle initial | |
| SSN | Text(11) | Social Security number | |
| Address1 | Text(50) | Address line 1 | |
| Address2 | Text(50) | Address line 2 | |
| City | Text(50) | City | |
| State | Text(2) | State | |
| ZipCode | Text(10) | Zip Code | |
| HomePhone | Text(50) | Employee's home phone number | |
| CellPhone | Text(50) | Employee's mobile phone number | |
| EmergencyContact | Text(50) | Name of person to contact in emergency | |
| EmergencyPhone | Text(50) | Emergency phone number | |
| HireDate | Date/Time | Date employee was hired | |
| Password | Text(50) | Employee password |
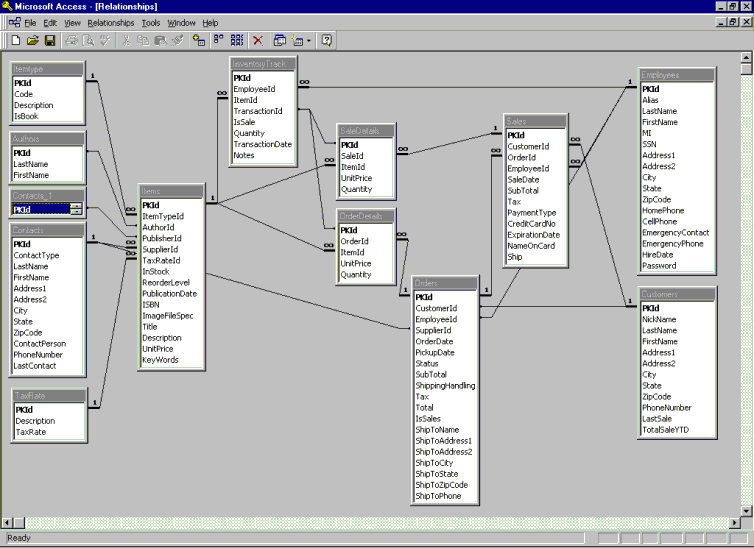
The relational database model provides efficient storage, simplifies data maintenance, and allows open-ended header detail structures. Item entities have relationships with other entity types, including references to an ItemType entity (required), Author entity (optional), Contact entity (for publisher and supplier), and TaxRateId (required). Enforced referential integrity ensures that relationships between entities remain valid as data changes. If Item entities contain references to an ItemType entity and that ItemType record is deleted, items that hold references to the deleted ItemType would violate relational integrity by referring to a deleted record. The .mdb database format holds referential integrity rules and the relationships are enforced by Microsoft Access, and by Microsoft Data Access technologies such as Microsoft ActiveX® Data Objects (ADO). Figure 1 shows the entity relationships within the data model.

Figure 1. Entity relationships
The database model presented here emphasizes simplicity over complete normalization or optimization. The data entities model the business processes of the bookstore in a direct manner that simplifies application programming but leaves some scalability issues to be resolved in subsequent phases. The next three project phases will present refinements to this design so that it can scale from supporting a few users on a desktop or local workgroup to support a high-volume Web-based enterprise system.