Visual Basic Concepts
It’s important to distinguish between the events received by your UserControl object (or by the controls it contains) and the events your control raises. Events your control receives are opportunities for you to do something interesting; events your control raises provide opportunities for the developer who uses your control to do something interesting.
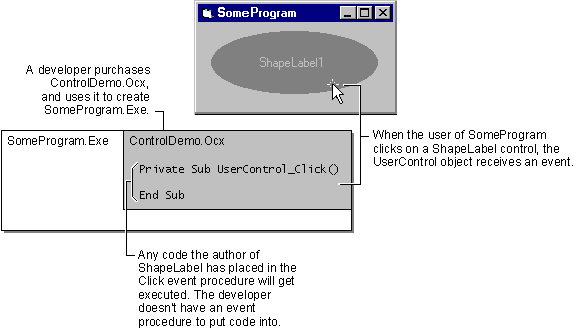
Figure 4.1 shows what happens when a control author simply uses the events received by the UserControl object, and doesn’t raise any events for the developer who buys the control.
Figure 4.1 An ActiveX control that simply uses events

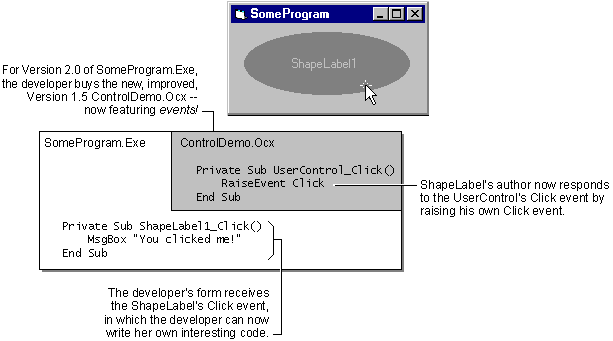
Figure 4.2 shows what happens when the author of ControlDemo.ocx — no doubt tired of developer complaints — improves the ShapeLabel control by raising a Click event for the developer to respond to.
Figure 4.2 A control that raises events for the developer to use
There are many events that might be of interest to the user of the ShapeLabel control. The Visual Basic Label control raises a Click event, and ShapeLabel is just a fancy label, so the following procedure will add a Click event. To make the event more interesting, it will be raised only if the user clicks on the oval background.
Being compatible with other controls of the same type is an important reason to add a particular event to your control. Other criteria for choosing what events to raise can be found in "Raising Events from Controls," in "Building ActiveX Controls."
Note This topic is part of a series that walks you through creating a sample ActiveX control. It begins with the topic Creating an ActiveX Control.
To add a Click event to the ShapeLabel control
Option Explicit
' Declare a public Click event with no arguments.
Public Event Click()
Private Sub lblCaption_Click()
' Raise a Click event whenever the user clicks
' on the label.
RaiseEvent Click
End Sub
The code above raises a Click event only if the user clicks on the constituent control lblCaption. It will seem more natural to users to be able to click anywhere on ShapeLabel’s oval background, so the next step shows how to raise the click event if the user clicks on the colored oval.
Private Sub UserControl_MouseUp(Button As Integer, _
Shift As Integer, X As Single, Y As Single)
' Raise a Click event only if the color of the
' point that was clicked on matches the color
' of the Shape control. Ignore clicks that are
' outside the oval.
If Point(X, Y) = shpBack.FillColor Then
RaiseEvent Click
End If
End Sub
Determining whether an event occurred in a particular location is called hit testing.
You might expect to put the hit test code in the shpBack_Click event procedure, because shpBack is always resized to cover the entire surface of the ShapeLabel control. However, Shape controls don’t receive Click events. Instead, the Click event is received by the object that contains the Shape — in this case, the UserControl object.
"Drawing Your Control," in "Building ActiveX Controls," discusses the use of transparent backgrounds to create irregularly shaped controls.
Note If the Click event does not appear, make sure the ShapeLabel designer is closed.
Add the following code to the ShapeLabel1_Click event procedure:
Private Sub ShapeLabel1_Click()
MsgBox "Thanks for clicking! My caption is: " _
& ShapeLabel1.Caption
End Sub
Note If the ShapeLabel you selected is not named ShapeLabel1, use the appropriate name when entering the code above.
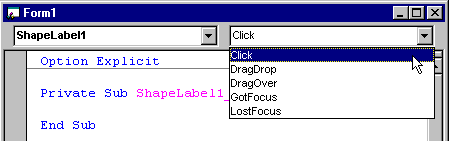
You can click the arrow on the Procedure box to view all of the events for the ShapeLabel control. In addition to your Click event, there are four events — DragDrop, DragOver, GotFocus, and LostFocus — that are automatically provided for you by the container, Form1.
The lblCaption_Click event procedure doesn’t get executed, because the MouseDown event occurred over the UserControl. Therefore, when the MouseUp event occurs, it is received by the UserControl — even if the mouse has been moved completely off Form1.
The hit test code in the MouseUp event works if the mouse button is released over the red background that shows through lblCaption’s transparent background, but not if the button is released over the white foreground color of the text. (If the button is released outside ShapeLabel, the Point function returns -1, so releasing the mouse button over some random red spot will not raise the Click event.)
Fixing this bug is left as an exercise for the reader. (Hint: Moving the hit test to the Click event of the UserControl won’t help, because the Click event doesn’t occur when the MouseUp event is over a different object from the MouseDown.)
For More Information See "Adding Events to Controls" in "Building ActiveX Controls."
This topic is part of a series that walks you through creating a sample ActiveX control.
| To | See |
| Go to the next step | Compiling the ControlDemo Component |
| Start from the beginning | Creating an ActiveX Control |