Visual Basic Concepts
You can build libraries of general-purpose procedures in Visual Basic by making the procedures methods of a class module. Set the Instancing property of the class module to any value except Private or PublicNotCreatable, so that clients can create instances of the class.
When you choose the value GlobalMultiUse for the Instancing property of a class, and then make the project, you can subsequently use the properties and methods of the class without having to explicitly create an instance of the class.
Properties and methods of a GlobalMultiUse object (or global object) are added to the global name space of any project that uses the object. That is, in another project you can set a reference to the component, and the names of the global objectís properties and methods will be recognized globally, just as if they were part of Visual Basic.
Important The properties and methods of a global object only become part of the global name space when the component is referenced from other projects. Within the project where you created the GlobalMultiUse class module, objects created from the class are just ordinary objects.
The following code fragments show the difference between using MultiUse and GlobalMultiUse objects. Both assume that youíve used the References dialog box to set a reference to a component that provides a Financials object whose methods are general-purpose financial functions.
Code required to use a MultiUse Financials object:
' This code goes in a standard module.
' Declare a global variable to contain the instance.
Public gfins As New Financials
' This code goes in a form that uses a method of the
' Financials object.
Private Sub cmdCalculateResult_Click()
txtResult.Text = gfins.LeastReasonableReturn( _
CCur(txtBeginningBalance.Text))
End Sub
Note When you use the code above, the Financials object is created the first time the variable gfins is used in code. This incurs a slight increase in overhead on each function call. You can avoid this by explicitly creating the Financials object in Sub Main (for standalone executables) or on first object creation (for components).
By contrast, the code to use a GlobalMultiUse Financials object requires no global variable:
Private Sub cmdCalculateResult_Click()
txtResult.Text = LeastReasonableReturn( _
CCur(txtBeginningBalance.Text))
End Sub
Visual Basic creates a hidden instance of the Financials class the first time a line of code containing one of its methods is executed.
Note As explained later in this topic, the hidden instance incurs the same slight overhead per call as declaring gfins As New in the previous code example.
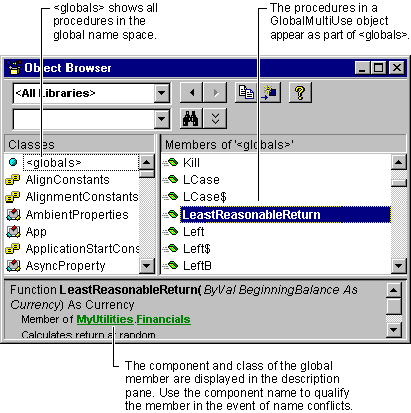
In the Object Browser, procedures that are part of a projectís global name space are displayed in the <globals> entry in the Classes list. Figure 8.1 shows this for a project group that uses the Financials class.
Figure 8.1 Methods of a GlobalMultiUse class appear in <globals>

The Object Browser displays the names of classes and members defined in your projects in bold type.
Tip You can move directly to the code that defines classes and members by double-clicking names displayed in bold type.
Setting the Instancing property of a class to GlobalMultiUse or GlobalSingleUse allows client programs to use the properties and methods of the class as if they were global functions, but within the project where you defined the GlobalMultiUse class module, objects created from the class are not global.
For example, suppose your MyUtilities project contains a Utilities class whose Instancing property is set to GlobalMultiUse, and that the class has an InvertMatrix method. Any client project that has a reference to MyUtilities can call InvertMatix as if it were a global function. However, within the MyUtilities project, you cannot use InvertMatrix as if it were a global function.
If you want to use a global instance of the Utilities class within the MyUtilities project, you can add the following declaration to a standard module in MyUtilities:
Public Utilities As New Utilities
Thereafter, whenever you need to use InvertMatrix (or any other procedure supplied by the Utilities class), you can qualify it with the class name:
Utilities.InvertMatrix aintMyLargeMatrix
The first time you use a method of the Utilities class in this fashion, an instance of the class is created automatically, because the global variable is declared As New. Using the class name as the name of the variable makes it clear which of the modules within your component is supplying the procedure.
Note You must declare the global variable in a standard module, not a class module, in order for this technique to work.
Visual Basic has properties of its <globals> that are themselves objects ó for example, the App object and the Printers collection. You can create similar object properties for your own global classes.
Suppose youíve created a Registry class for accessing the Windows registry, and that you have a Globals class whose Instancing property is GlobalMultiUse. The following code fragment shows how you can add a Registry property to your Globals class:
Private mRegistry As Registry
Private Sub Class_Initialize()
Set mRegistry = New Registry
End Sub
Public Property Get Registry() As Registry
Set Registry = mRegistry
End Sub
Once youíve compiled your component, you can reference it from other projects. If the Registry class includes a FindKeyContaining method, you might write code like this to use it:
Private Sub Command1_Click()
lblResult.Caption = _
Registry.FindKeyContaining(txtInput.Text)
End Sub
This code assumes that the form contains a text box in which the user enters a string to be located (txtInput), and a label in which the registry key is displayed (lblResult). Notice that you didnít have to create an instance of Globals before using the Registry object.
Tip Always use Property Get when you add an object property to your global object. If you use a public variable instead, you can accidentally destroy the object the property provides by setting the property to Nothing.
You may find the following useful in getting the most out of global objects:
For example, suppose you were using both MyUtilities and YourUtilities, and that YourUtilities had a GlobalMultiUse class named General that also included a method named LeastReasonableReturn. You would code the following to ensure that the method in YourUtilities was used:
Private Sub cmdCalculateResult_Click()
txtResult.Text = _
YourUtilities.LeastReasonableReturn( _
CCur(txtBeginningBalance.Text))
End Sub
Important If conflicting names are not qualified, Visual Basic uses the library that appears highest in the References dialog box. Unless the procedures have different arguments, no compile-time errors occur.
Important Global name space pollution is a serious issue. For an example and discussion, see "Creating a Reference to an Object," in "Programming with Components," in the Visual Basic Programmerís Guide.
Important Each client that uses the properties and methods of a GlobalMultiUse class gets its own instance of the class. In other words, the "Global" in GlobalMultiUse does not mean "one global instance that all clients share."
When youíre deciding whether to use a global object or explicitly declare a variable to hold an instance of an object, the following may be of use:
For out-of-process components only, you can set the Instancing property of a class module to GlobalSingleUse. If you do this, a separate instance of your component will be loaded into memory for each client. This requires a lot more memory than providing GlobalMultiUse objects.
If you simply want each client to have a separate thread of execution for your global procedures, consider using GlobalMultiUse for your global objects and making your out-of-process component multithreaded, as described in "Scalability and Multithreading."
Note GlobalSingleUse is not allowed in ActiveX DLL projects, because multiple instances of a DLL cannot be loaded into a clients process space.
For More Information See "Scalability Through Multiple Processes: SingleUse Objects."