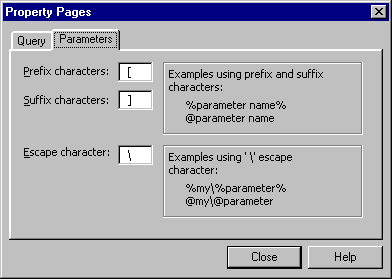
To mark a name as a parameter and not as a string of literal characters, you place a prefix in front of the parameter name (and, as an option, a suffix after it). For example, parameter marker characters might be "@", ":", or "%". Typically, you use the parameter marker character recognized for your database. For details about what parameter marker characters you need, refer to the documentation for your database or environment.
Note If you are querying a SQL Server or Oracle database, the Query Designer will automatically fill in the correct parameter marker character as the default in the Parameters tab.
For example, in your query you might define a parameter called "last name." To indicate that "last name" is a parameter and not a string to search for in the lname column, you might specify that the parameter marker characters are "[" and "]". You can then enter "[last name]" as a search condition value, and the Query Designer will correctly interpret "last name" as a parameter.
In rare instances, the parameter marker character you define might also appear in the name of the parameter. If so, you can specify an escape character. For details, see Parameters Tab, Properties Window.
To specify parameter marker characters
