Security
|

|
Troubleshooting Permissions
As you can see, access to resources such as files and databases can be a complex issue when you are securing your Web server. Site administrators often work blindly when trying to troubleshoot access problems. Monitoring how the server is being used is a good place to start, which requires you to set up auditing.
The following outlines how to set up auditing and logging for troubleshooting.
To set up auditing for user logons and file access
- Open the Global Policy Editor for the computer or domain in question.
- Go to Computer Configuration, Windows Settings, Security Settings, Local Policies and then Audit Policy.
- Set Audit successful attempts and Audit failed attempts to Yes under the Audit Logon Events category.
- Set Audit failed attempts to Yes under the Audit Object Access category.
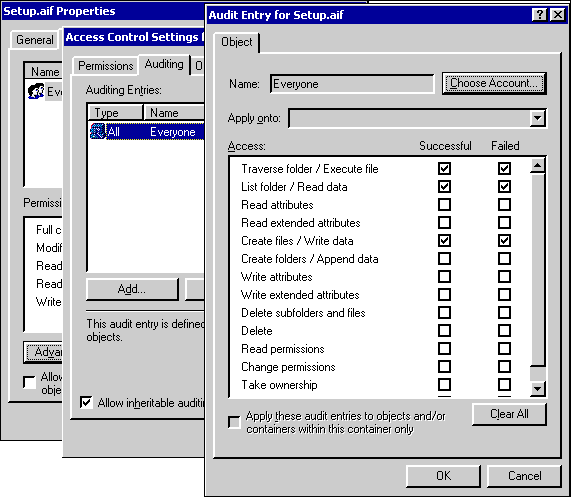
To choose the file to audit
- Open Windows Explorer.
- Select the file or folder that you want to audit.
- Right-click the file or folder and select Properties.
- Click the Security tab and the Advanced button, and then click the Auditing button.
- Click the Add button.
- Select Everyone, click Add, and then click OK.
- Select Successful and Failed for the following:
- Traverse folder/Execute file
- List folder/Read data
- Create files/Write data
- Click OK.
Much of this process is shown in the following figure.
To enable Web Logging
- Open the Computer Management administration tool.
- Click Server Applications and Services to expand it and click IIS 5.0 to do the same.
- Select the Web server in question.
- Right-click on the Web site and select Properties.
- Select Enable Logging.
- Click the Properties button.
- Click the Extended Properties tab.
- Select (at least) the following: Date, Time, Client IP Address, User Name, Method, HTTP status, and Win32 status.
- Click OK to exit the logging properties.
- Click OK to exit the Web site properties.
- Now that basic auditing is in place, clear any cached logon information (remember, for performance purposes IIS 5.0 can cache logon information) by typing the following at the command prompt:
NET STOP IISADMIN /Y This stops all IIS 5.0 services.
NET START W3SVC This starts the Web service, if installed.
NET START MSFTPSVC This starts the File Transfer Protocol (FTP) service, if installed.
NET START NNTPSVC This starts the Network News Transfer Protocol (NNTP) service, if installed.
NET START SMTPSVC This starts the Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP) service, if installed.
- Open the Event Viewer.
- Clear the Security log by right-clicking the Security log and selecting Clear all events.
See the following:
© 1997-1999 Microsoft Corporation. All rights reserved.
