Security |
Client certificates contain information that identifies the user, as well as information about the organization that issued the certificate. For example, a standard X.509 certificate contains at least the following:
The following figure shows an example of a client authentication certificate in Microsoft® Internet Explorer 5:
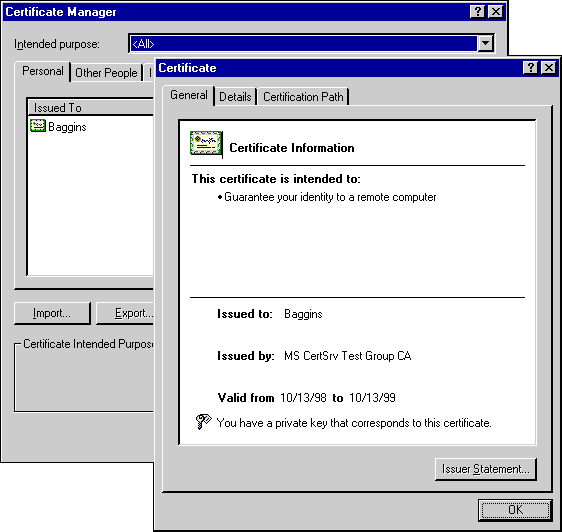
A user obtains a client certificate from a trusted third-party organization such as VeriSign (http://www.verisign.com) or Thawte Consulting (http://www.thawte.com). These organizations are usually referred to as certification authorities or CAs. You can find a more complete list of CAs at http://www.microsoft.com/security/ca/ca.htm.
If you have Microsoft® Windows® 2000 Certificate Services installed, your site can issue its own certificates to users on the intranet or to business partners.