Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol
|
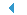

|
How the Lease Process Works
The first time a DHCP-enabled client starts and attempts to join the network, it automatically follows an initialization process to obtain a lease from a DHCP server. Figure 4.2 shows the lease process.
Figure 4.2 The DHCP Lease Process
- The DHCP client requests an IP address by broadcasting a DHCPDiscover message to the local subnet.
- The client is offered an address when a DHCP server responds with a DHCPOffer message containing an IP address and configuration information for lease to the client. If no DHCP server responds to the client request, the client can proceed in two ways:
- If it is a Windows 2000–based client, and IP auto-configuration has not been disabled, the client self-configures an IP address for its interface.
- If the client is not a Windows 2000–based client, or IP auto-configuration has been disabled, the client network initialization fails. The client continues to resend DHCPDiscover messages in the background (four times, every 5 minutes) until it receives a DHCPOffer message from a DHCP server.
- The client indicates acceptance of the offer by selecting the offered address and replying to the server with a DHCPRequest message.
- The client is assigned the address and the DHCP server sends a DHCPAck message, approving the lease. Other DHCP option information might be included in the message.
- Once the client receives acknowledgment, it configures its TCP/IP properties using any DHCP option information in the reply, and joins the network.
In rare cases, a DHCP server might return a negative acknowledgment to the client. This can happen if a client requests an invalid or duplicate address. If a client receives a negative acknowledgment (DHCPNak), the client must begin the entire lease process again.
© 1985-2000 Microsoft Corporation. All rights reserved.