Windows CE Services contains Microsoft ActiveSync™ technology, which provides data replication and synchronization. ActiveSync does this by comparing the data on a Windows CE–based device with the data on the desktop computer to which the device is connected. After comparing data, ActiveSync updates both the device and the desktop computer with the most recent information.
ActiveSync is composed of the service manager and the service provider. The service manager is a synchronization engine that is built into Windows CE Services and resides on both the desktop computer and the Windows CE–based device. The service provider comprises two modules that you must implement in your application to perform the synchronization tasks that are specific to your data. One module, called the desktop provider module, resides on the desktop computer and the other module, called the device provider module, resides on the device. By creating and registering the service provider, you decide which data is tracked for changes by the service manager. And by creating the proper file converters, you enable ActiveSync to maintain the same information on a device as on the desktop computer.
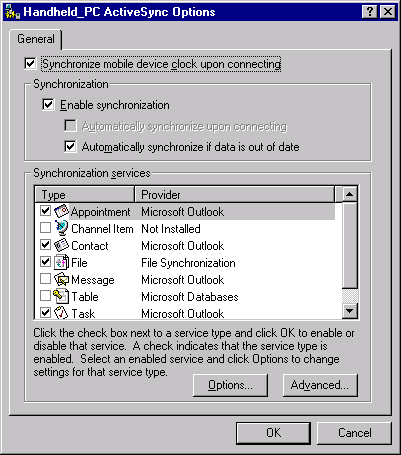
Built-in functionality gives users the option of choosing a subset of information to synchronize. For example, they can synchronize only e-mail, only certain files, only their Pocket Outlook data, or only certain categories of information that they define, such as business contacts or personal appointments. The following screen shot shows the ActiveSync Options page for the Handheld PC.

ActiveSync gives a user the option to synchronize data either manually, automatically on connection, or continuously while a connection is active so that changes appear immediately on both the device and the desktop computer. In addition, the user can synchronize both at their desktop computer and away from it, over serial, infrared, Ethernet LAN, and modem connections. Users can synchronize their device information with two desktop computers, such as their home and office computer, or they can synchronize information on one desktop computer with several devices—for example, to share files within a department.