 To create a scroll bar using CreateWindow
To create a scroll bar using CreateWindowA scroll bar is used to scroll text in a window. Scroll bars should be included in any window for which the content of the client area extends beyond the window borders. The orientation of a scroll bar determines the direction in which scrolling occurs when a user operates the scroll bar. A horizontal scroll bar enables a user to scroll the content of a window to the left or right. A vertical scroll bar enables a user to scroll the content up or down.
You can use as many scroll bar controls as needed in a single window. When you create a scroll bar control, you must specify the size and position of the scroll bar. However, if a scroll bar control's window can be resized, your application must adjust the size of the scroll bar when the size of the window changes.
 To create a scroll bar using CreateWindow
To create a scroll bar using CreateWindowA scroll bar control can have a number of styles to control the orientation and position of the scroll bar. Some of the styles create a scroll bar control that uses a default width or height. However, you must always specify the x and y coordinates and the scroll bar dimensions. For a complete listing of supported styles, see Window and Control Styles.
The following code example shows how to use CreateWindow to create a scroll bar.
#define SCROLLBARID 100
DWORD dwStyle = SBS_BOTTOMALIGN | SBS_HORZ | WS_VISIBLE | WS_CHILD;
hwndSB = CreateWindow (
TEXT("scrollbar"), // Class name
NULL, // Window text
dwStyle, // Window style
0, // x coordinate of the upper-left corner
0, // y coordinate of the upper-left corner
CW_USEDEFAULT, // The width of the edit control window
CW_USEDEFAULT, // The height of the edit control window
hwnd, // Window handle to parent window
(HMENU) SCROLLBARID,// The control identifier
hInst, // The instance handle
NULL); // Specify NULL for this parameter when
// creating a control
 To create a scroll bar control in a dialog box
To create a scroll bar control in a dialog boxSCROLLBAR id, x, y, width, height [[, style [[, extended-style]]]]
Here, id is the value that identifies the scroll bar.
The x and y parameters determine the scroll bar position and are represented as integers. They are relative to the left or upper end of the scroll bar, depending on whether the scroll bar is horizontal or vertical. The position must be within the minimum and maximum values of the scrolling range. For example, in a scroll bar with a range from 0 through 100, position 50 is the middle, with the remaining positions distributed equally along the scroll bar. The initial range depends on the scroll bar. Standard scroll bars have an initial range from 0 through 100. Scroll bar controls have an empty range—both minimum and maximum values are zero—unless you supply an explicit range when you create the control. You can alter the range at any time after its initial creation. You can use the SetScrollInfo function to set the range values and the GetScrollInfo function to retrieve the current range values.
The width and height parameters determine the scrollbar size. You can set a scroll bar equal to a page size. The page size represents the number of data units that can fit in the client area of the owner window given its current size. For example, if the client area can hold eight lines of text, an application would set the page size to eight. Windows CE uses the page size, along with the scrolling range and length of the scroll bar's gray area, to set the size of the scroll bar. When a window containing a scroll bar is resized, an application should call the SetScrollInfo function to set the page size. An application can retrieve the current page size by calling the GetScrollInfo function.
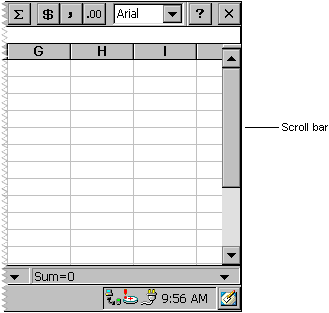
Style and extended-style determine the appearance of the edit box. The default style of a scroll bar is SBS_HORZ, which creates a horizontal scroll bar. The following screen shot shows a horizontal scroll bar. For a vertical scroll bar, specify the SBS_VERT style. For a complete listing of supported styles, see Window and Control Styles.
To establish a useful relationship between the scroll bar range and the data object, your application must adjust the range when the size of the data object changes.
As a user moves the scroll box in a scroll bar, the scroll bar reports the scroll box position as an integer in the scrolling range. If the position is the minimum value, the scroll box is at the top of a vertical scroll bar or at the left of a horizontal scroll bar. If the position is the maximum value, the scroll box is at the bottom of a vertical scroll bar or at the right end of a horizontal scroll bar.
Your application must move the scroll box in a scroll bar. Although a user makes a request for scrolling in a scroll bar, the scroll bar does not automatically update the scroll box position. Rather, it passes the request to the parent window, which must scroll the data and update the scroll box position. Use the SetScrollInfo function in your application to update the scroll box position. Because your application controls the scroll box movement relative to the window data object, you determine the incremental position settings for the scroll box that work best for the data being scrolled.