Union queries combine fields from two or more tables or queries into one field. Following are examples of a basic union query, and of sorting records, renaming fields, and returning duplicate records in union queries.
This topic provides information about:
Renaming fields in a union query
Returning duplicate records in a union query
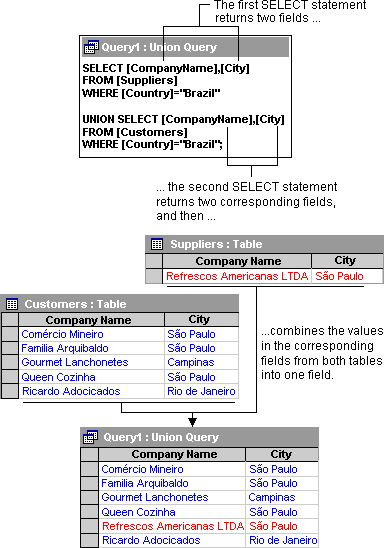
The following union query consists of two SQL SELECT statements that return the company names and cities that are in Brazil, from both the Suppliers and Customers tables.

Return to top
The following union query selects all company names and cities from both the Suppliers and Customers tables, and sorts the data alphabetically by city:
SELECT [CompanyName], [City]
FROM [Suppliers]
UNION SELECT [CompanyName], [City]
FROM [Customers]
ORDER BY [City];Return to top
The following union query renames the Company Name field to "Supplier/Customer Name" in the query output:
SELECT [CompanyName] AS [Supplier/Customer Name], [City]
FROM [Suppliers]
UNION SELECT [CompanyName] AS [Supplier/Customer Name], [City]
FROM [Customers];Return to top
The following union query uses the UNION ALL statement to retrieve all records, including duplicates:
SELECT [CompanyName], [City]
FROM [Suppliers]
UNION ALL SELECT [CompanyName], [City]
FROM [Customers];Return to top
Work with SQL in queries, forms, reports, macros, and modules
Ways to bring together data from multiple tables or queries in a query