Make a macro run under specific conditions
- In the Macro window, click Conditions
 on the toolbar.
on the toolbar.
- In the Condition column, type a conditional expression in the row where you want to set the condition.
Notes
- In the Action column, enter the action you want Microsoft Access to perform when the condition is true.
When you run the macro, Microsoft Access evaluates the first conditional expression. If the condition is true, Microsoft Access carries out the action in that row and all of the immediately following actions that are preceded by an ellipsis (...) in the Condition column. For example, the following macro carries out the MsgBox and StopMacro actions only when there is no value in the SupplierID field (when the value is Null).
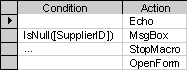
Microsoft Access then runs any additional actions in the macro that have a blank Condition column until it reaches another expression, a macro name, or the end of the macro.
If the condition is false, Microsoft Access ignores the action and any immediately following actions that are preceded by an ellipsis in the Condition column and moves to the next action row that contains another condition or a blank Condition column.
For examples of macro conditions, click  . For information on creating expressions, click
. For information on creating expressions, click  .
.
 on the toolbar.
on the toolbar. to use the Expression Builder. The Expression Builder is not available from a Microsoft Access project.
to use the Expression Builder. The Expression Builder is not available from a Microsoft Access project.
