This topic provides reference information about:
Forms, subforms, and subdatasheets
Comparing subdatasheets in a Microsoft Access database and a Microsoft Access project
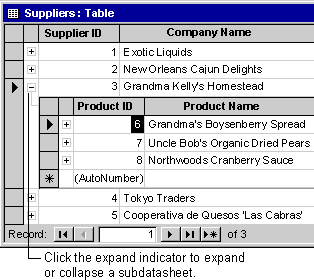
In a subdatasheet, you can view and edit related or joined data in a table, query, or form datasheet, or in a subform. For example, in the Northwind sample database the Suppliers table has a one-to-many relationship with the Products table; so for each row of the Suppliers table in Datasheet view, you can view and edit the related rows of the Products table in a subdatasheet.

Return to top
Access automatically creates a subdatasheet in a table that is in a one-to-one relationship, or is on the "one" side of a one-to-many relationship, when the SubdatasheetName property of the table is set to Auto. A relationship is defined by matching primary key and foreign key fields in the related tables. Learn about defining relationships.
However, you can add a subdatasheet to any table, query, or form. A subdatasheet can have as its source object a table or query (specified in the SubdatasheetName property). A subdatasheet corresponding to a subform control can have as its source object a table, query, or form (specified in the subform control's SourceObject property).
Return to top
Both a table and a query in Datasheet view can contain either a table or query subdatasheet. If a table has a one-to-many relationship with more than one other table, you can choose which table to add as a subdatasheet by clicking the expand indicator icon (+) and selecting a table in the Insert Subdatasheet dialog box.
By default, Access does not display the foreign key or matching field(s) in the subdatasheet. You can temporarily show the foreign key or matching field(s) by using the Unhide Columns command (Format menu), but the next time you open the datasheet containing the subdatasheet, the column(s) will be hidden again. Hiding or showing these fields changes only the appearance of the subdatasheet; it does not modify any relationship or source object.
You can add a subdatasheet to a table or query in Datasheet view, or modify a subdatasheet, by using the Subdatasheet command (Insert menu). You specify the matching fields between the datasheet and subdatasheet in the List Child Fields and Link Master Fields boxes in the Insert Subdatasheet dialog box. These boxes correspond to the LinkChildFields and LinkMasterFields properties of the table or query containing the subdatasheet. If you leave these boxes blank, Access displays all rows of the subdatasheet under every row in the datasheet, not just the rows in the subdatasheet that match.
Return to top
You can nest (up to eight levels) a subdatasheet within a subdatasheet. However, each datasheet or subdatasheet can have only one nested subdatasheet. For example, in the Northwind sample database, the Customers table can contain one Orders table subdatasheet, and the Orders table subdatasheet can contain one Orders Details subdatasheet. But the Customers table can't contain both an Orders table subdatasheet and a Salespeople query subdatasheet.
Return to top
A form in Form view or Datasheet view can also have a subdatasheet, but there are differences between a form subdatasheet and a table or query subdatasheet:
Return to top
You can use a table or query subdatasheet only in a Microsoft Access database, not in a Microsoft Access project. However, you can use a subdatasheet in a subform or in form Datasheet view in both an Access database and an Access project.
Return to top
Insert or modify a subdatasheet in a table or query in an Access database
Return to top